لين ماب دريكسلر(1928-1999)





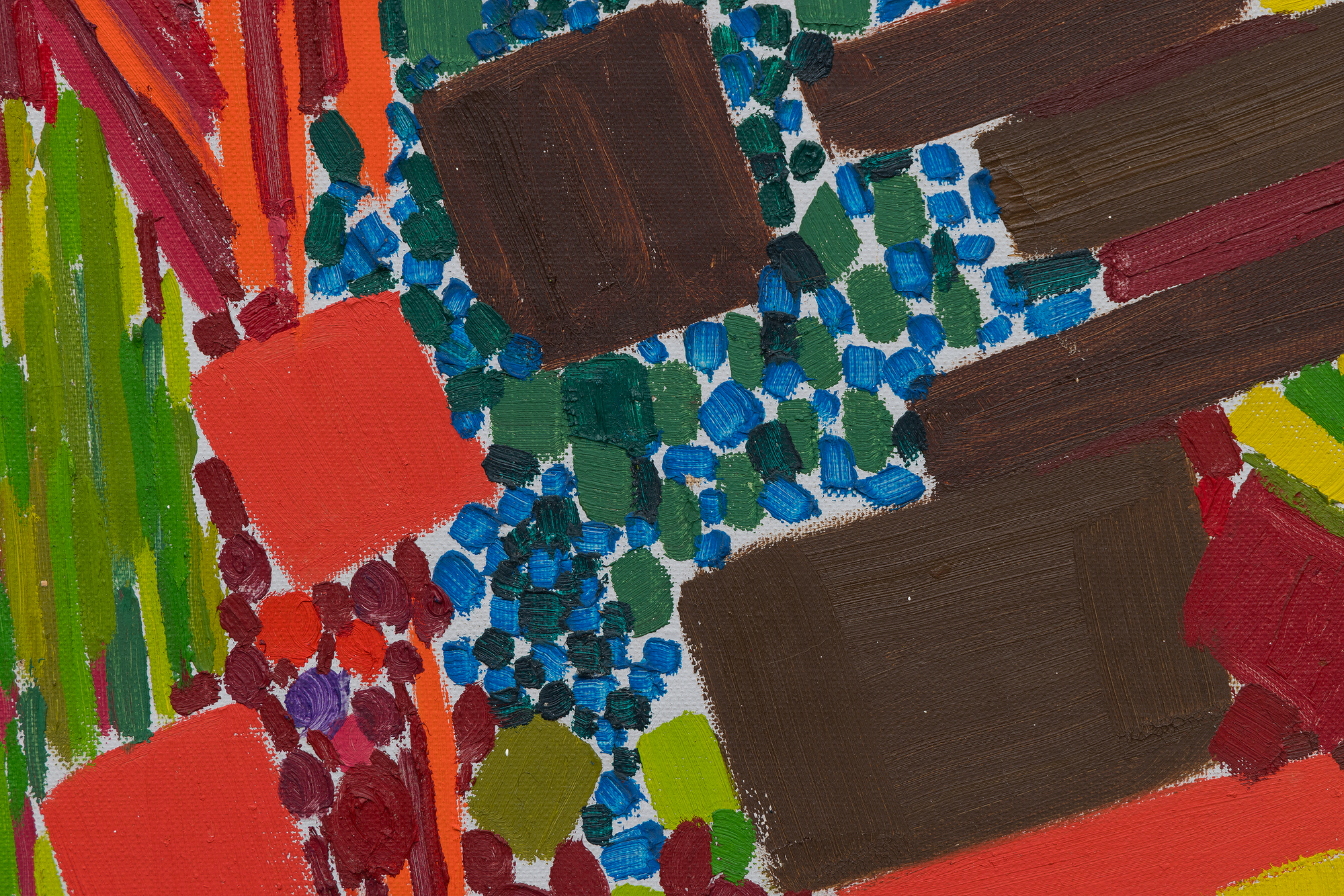




الاصل
معرض لوبين، مونهيجان، مينمجموعة خاصة، تم اقتناؤها من المجموعة المذكورة أعلاه
فيليبس نيويورك، الأربعاء 15 نوفمبر 2023، نوفمبر 2023، القطعة 106
مجموعة خاصة، تم الحصول عليها مما سبق
السعر375,000
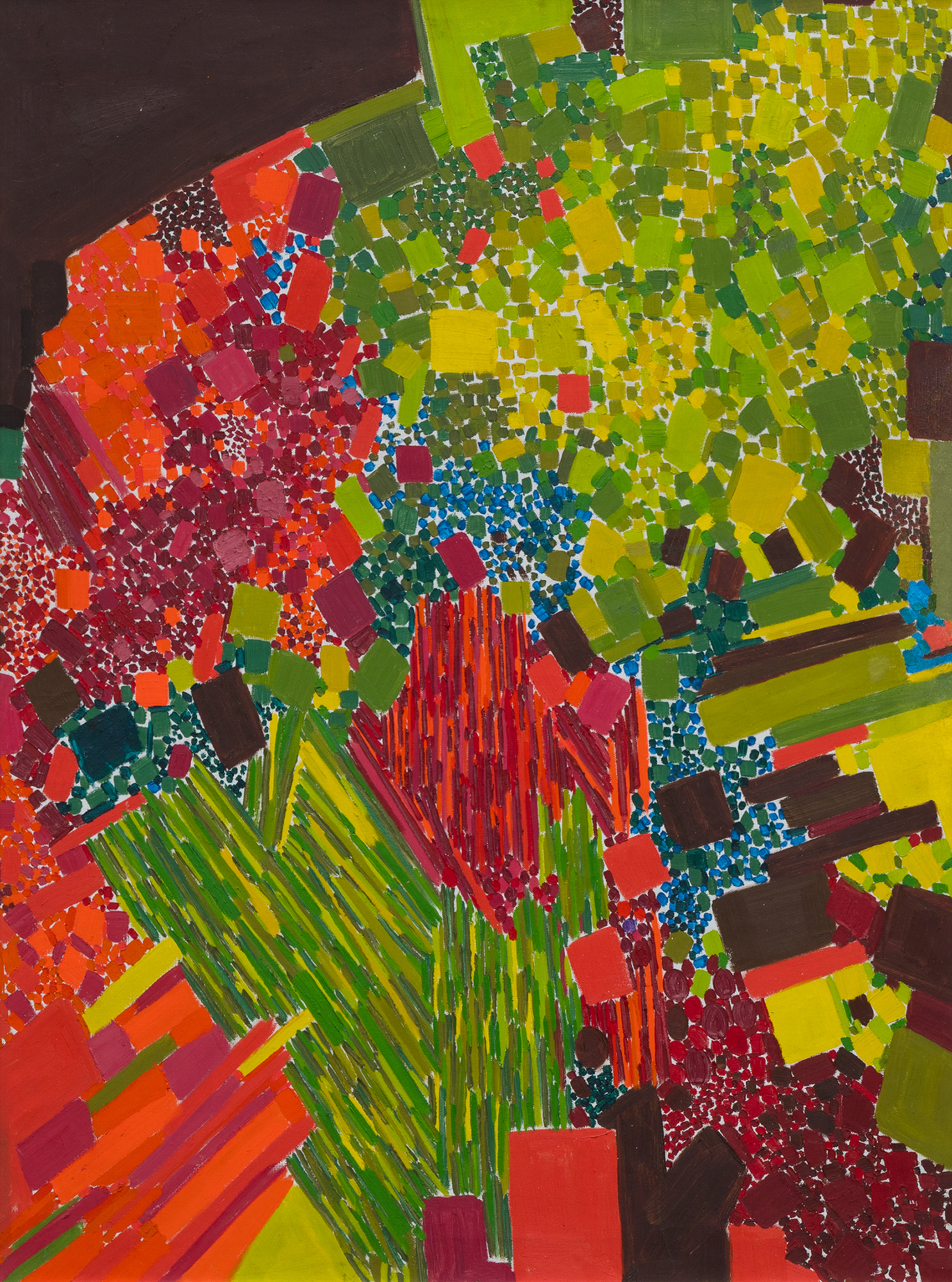
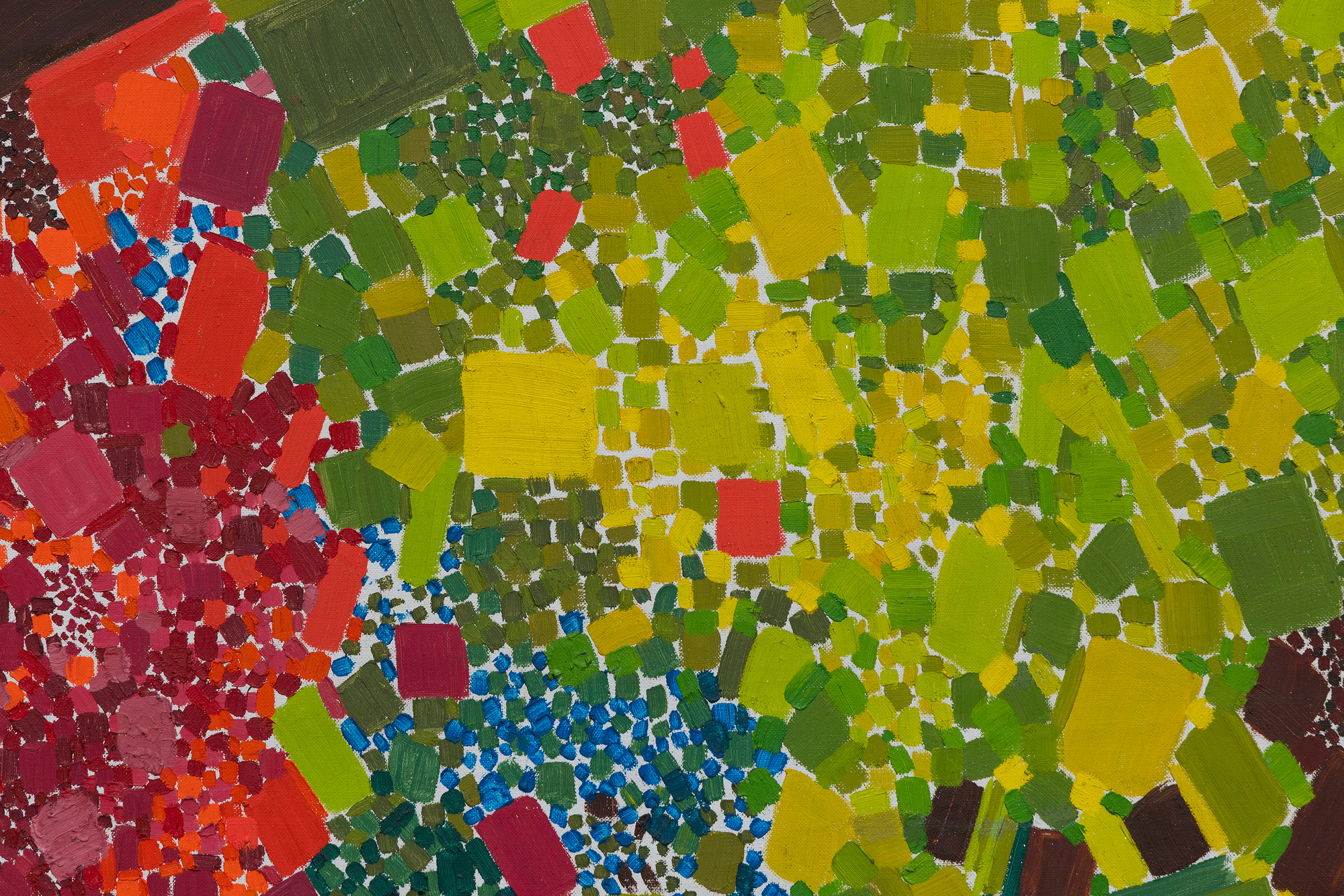
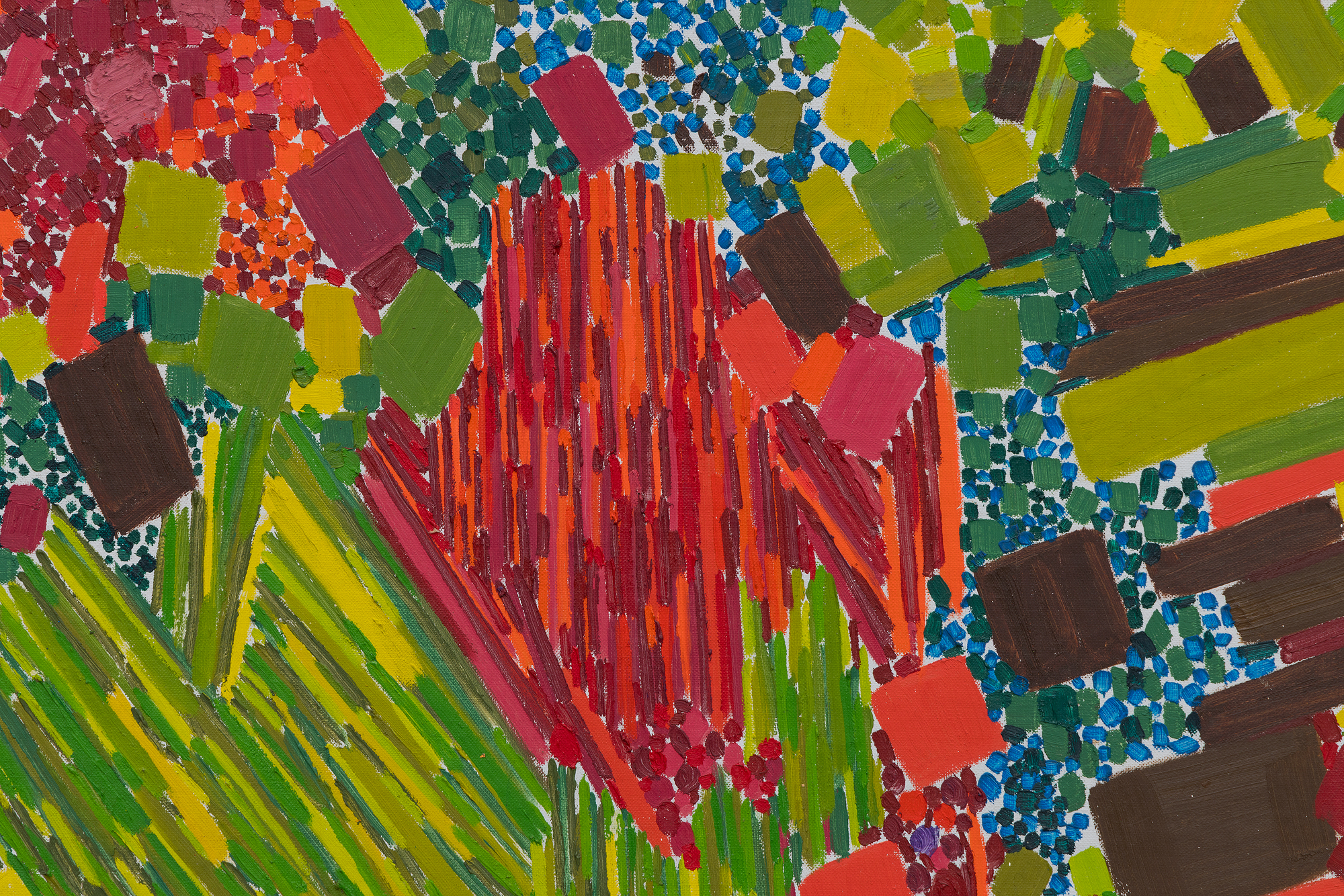
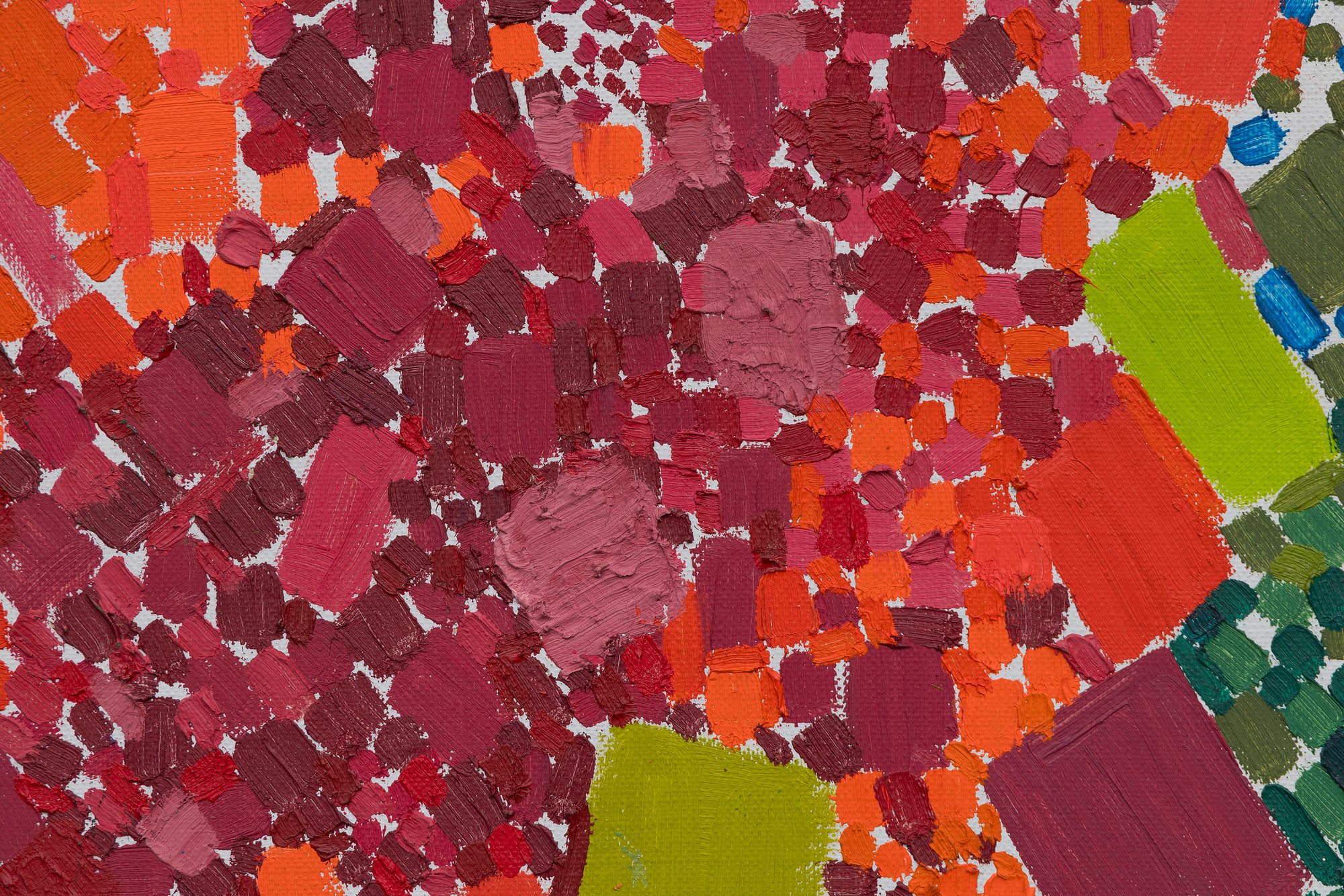
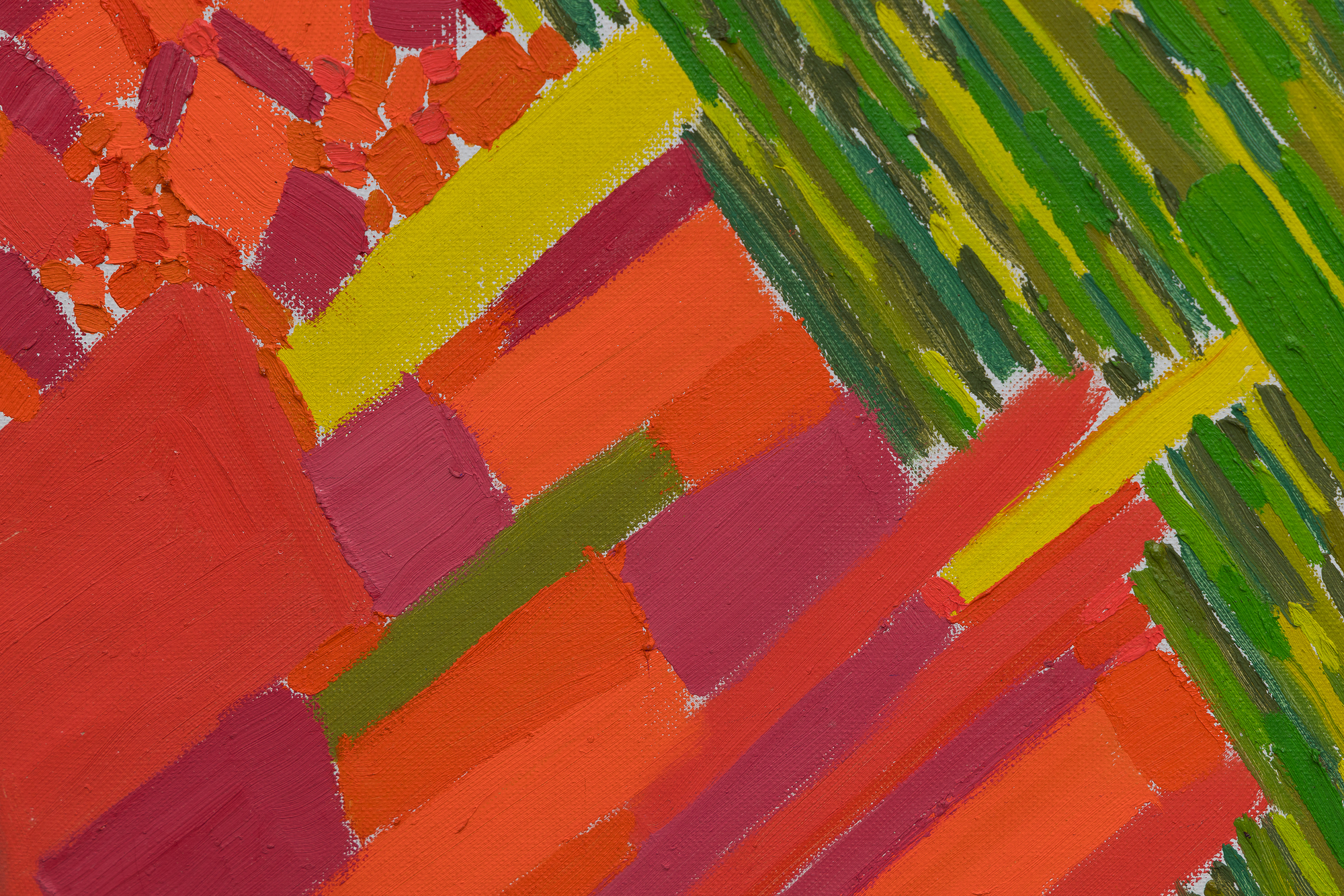
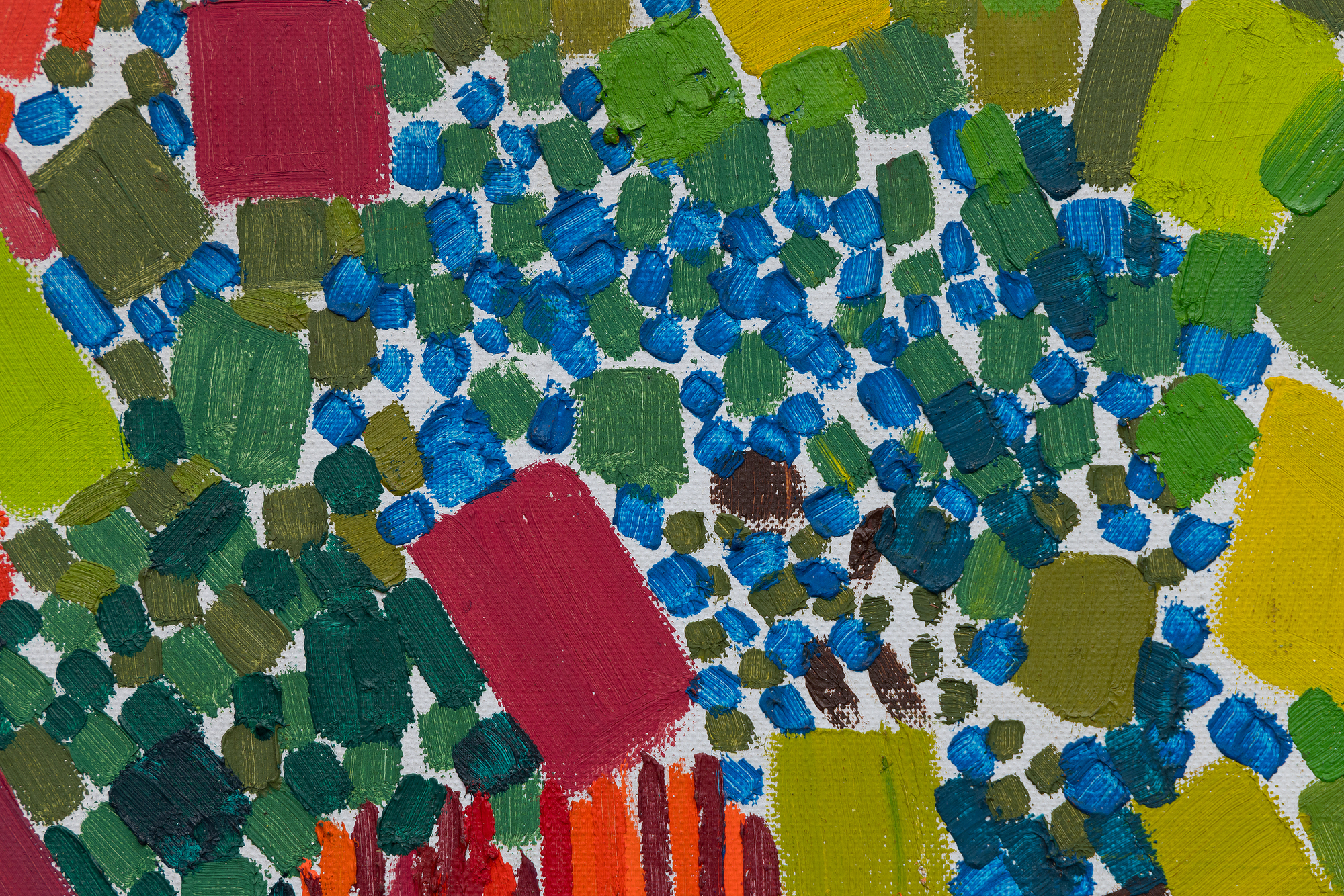
في هذا العمل، يحتل اللون الأسبقية على الشكل، حيث تستخدم دريكسلر الكثافة اللونية لخلق الإيقاع والبنية. يتناغم أسلوبها مع نظرية "الدفع والسحب" المؤثرة لهانز هوفمان، حيث تولد العلاقات اللونية العمق المكاني والتوتر دون الاعتماد على المنظور التقليدي. وفي الوقت نفسه، تعكس الحيوية الإيمائية والجودة الارتجالية لعمل الفرشاة تأثير معلمها روبرت ماذرويل، الذي شجع الحرية التعبيرية والفورية العاطفية.
تجسد لوحة "ربيع متقطع" توليفة دريكسلر بين الانضباط والعفوية، وتكشف كيف صاغت صوتاً متميزاً داخل مدرسة نيويورك بينما كانت تستبق التجريد الغنائي الذي سيحدد أسلوبها الناضج.


