中国語
$300,000






出所
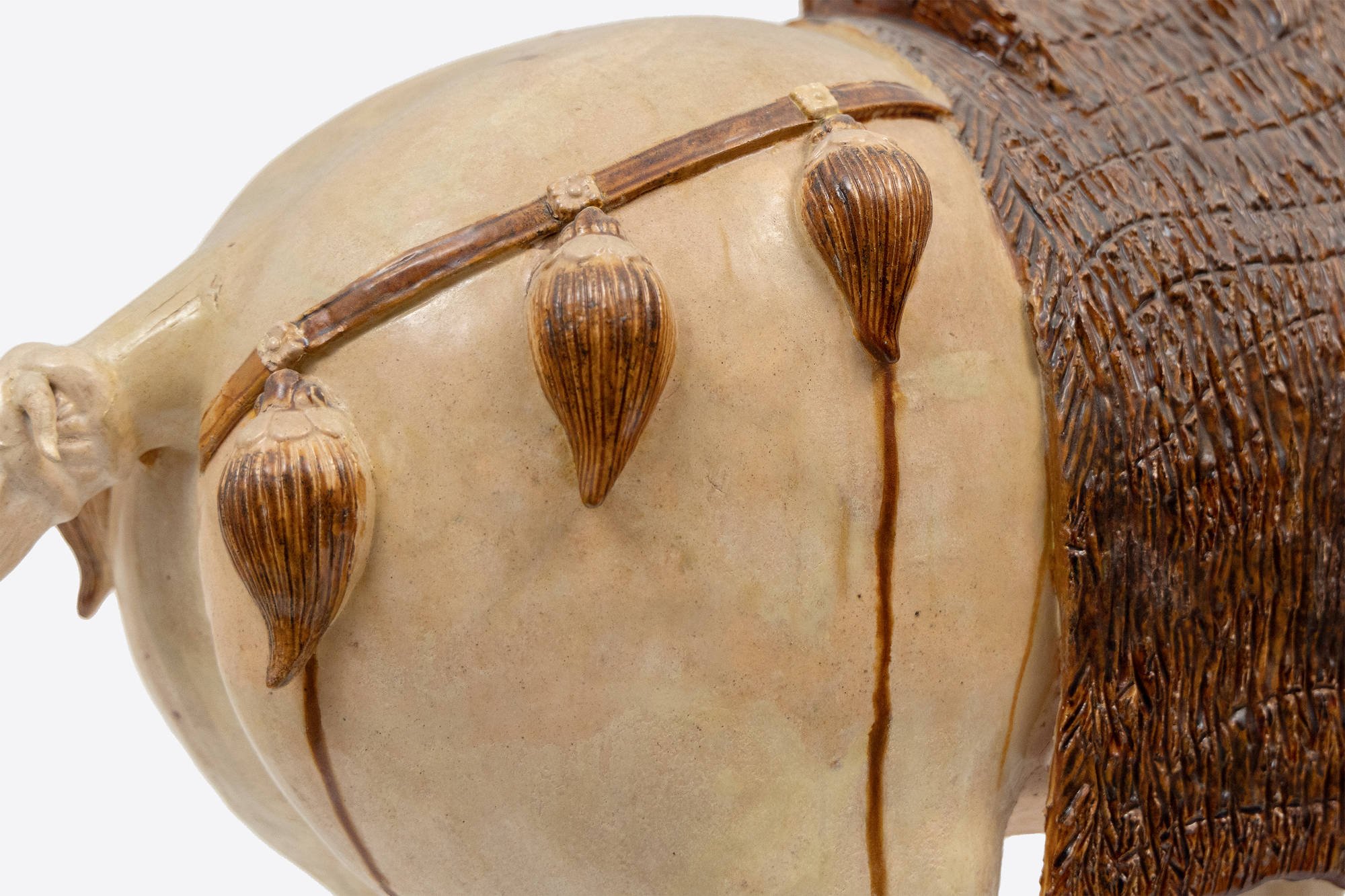
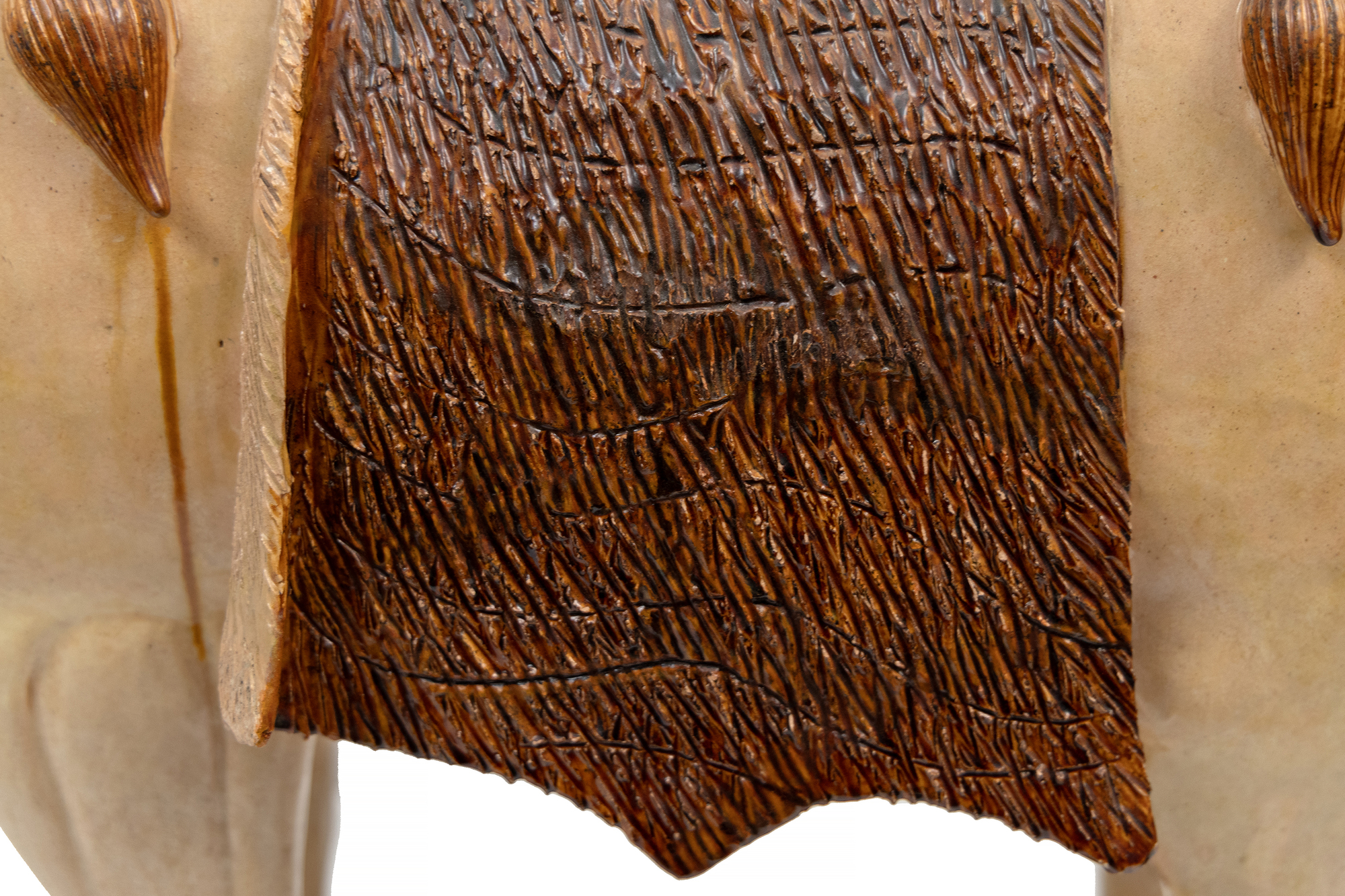
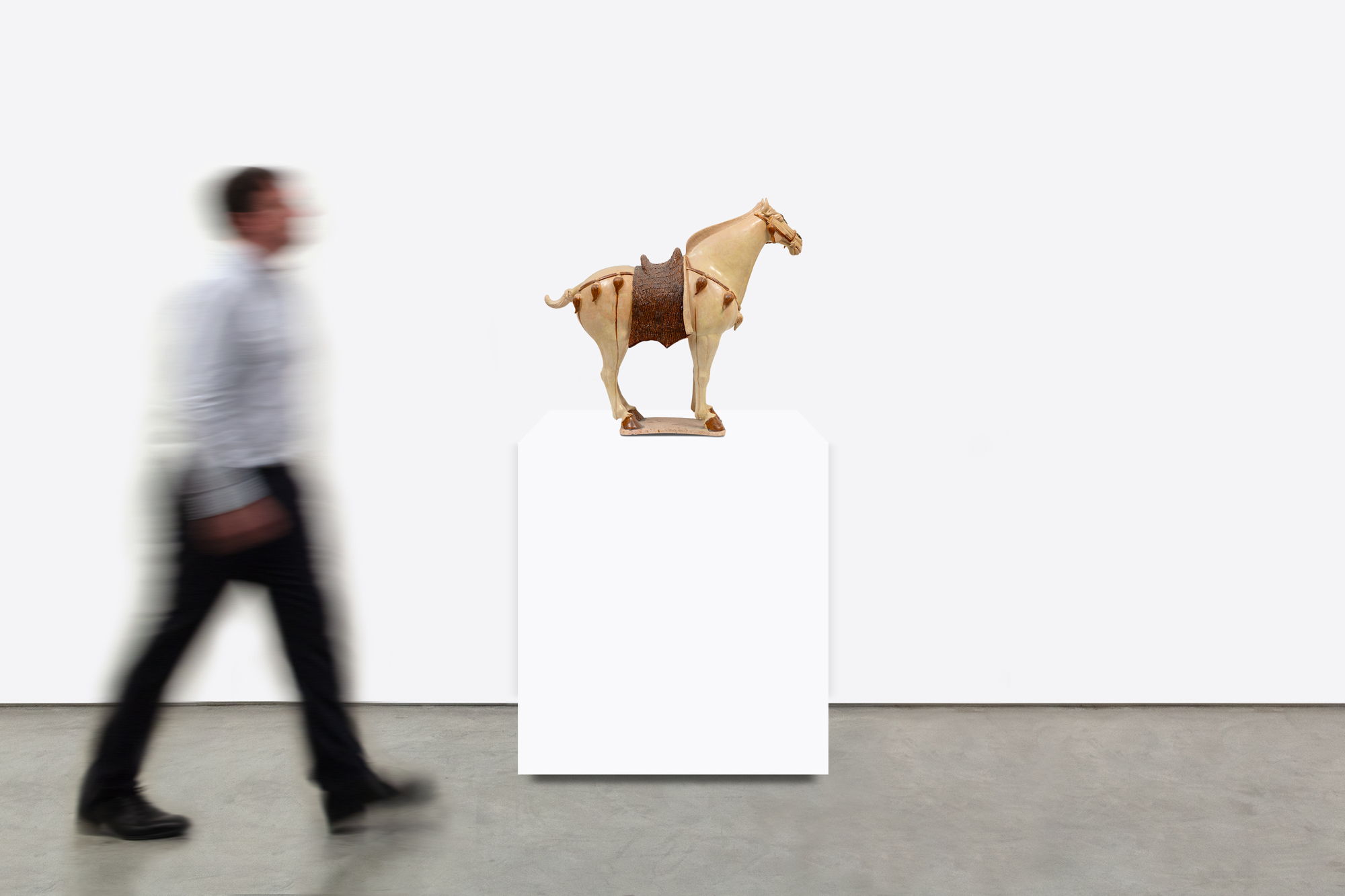
プライベートコレクション (カリフォルニア州)何世紀にもわたる伝統を守りながら、葬儀は非常に重要なものであり続けていました。葬儀用品の製造を監督する責任を持つ独立した政府部門が存在していました。公式には、官位に応じて墓用品の数に制限があり、故人に添える物の大きさにも制限がありました。最高位の官吏は高さ30cm以下の置物を90個まで、皇族は高さ約1mまでの物を数百個までとされていました。しかし、このルールは頻繁に破られていました。故人の親族は、必要以上に明器を提供することで、死後の世界で先祖の地位を向上させ、自分たちの幸運を保証できると信じていました。唐代の具象陶磁には独特の特徴があります。形は生き生きとしていて生命感があり、社会生活や祭祀生活のあらゆる側面を対象としています。廷臣や芸能人、ポロ選手、ラクダを引き連れて定期的に中国の都市にやってくる異国情緒あふれる旅行者などの人物像はよく見かけるようになり、時代の国際性を物語っています。このように様々な形のものがあることは、職人たちには個々の革新の余地があり、特定のスタイルに関するルールに縛られていなかったことを物語っています。今では、葬儀用品は権力や軍事力だけでなく、故人の洗練された知的業績をも物語っています。


