パーム砂漠
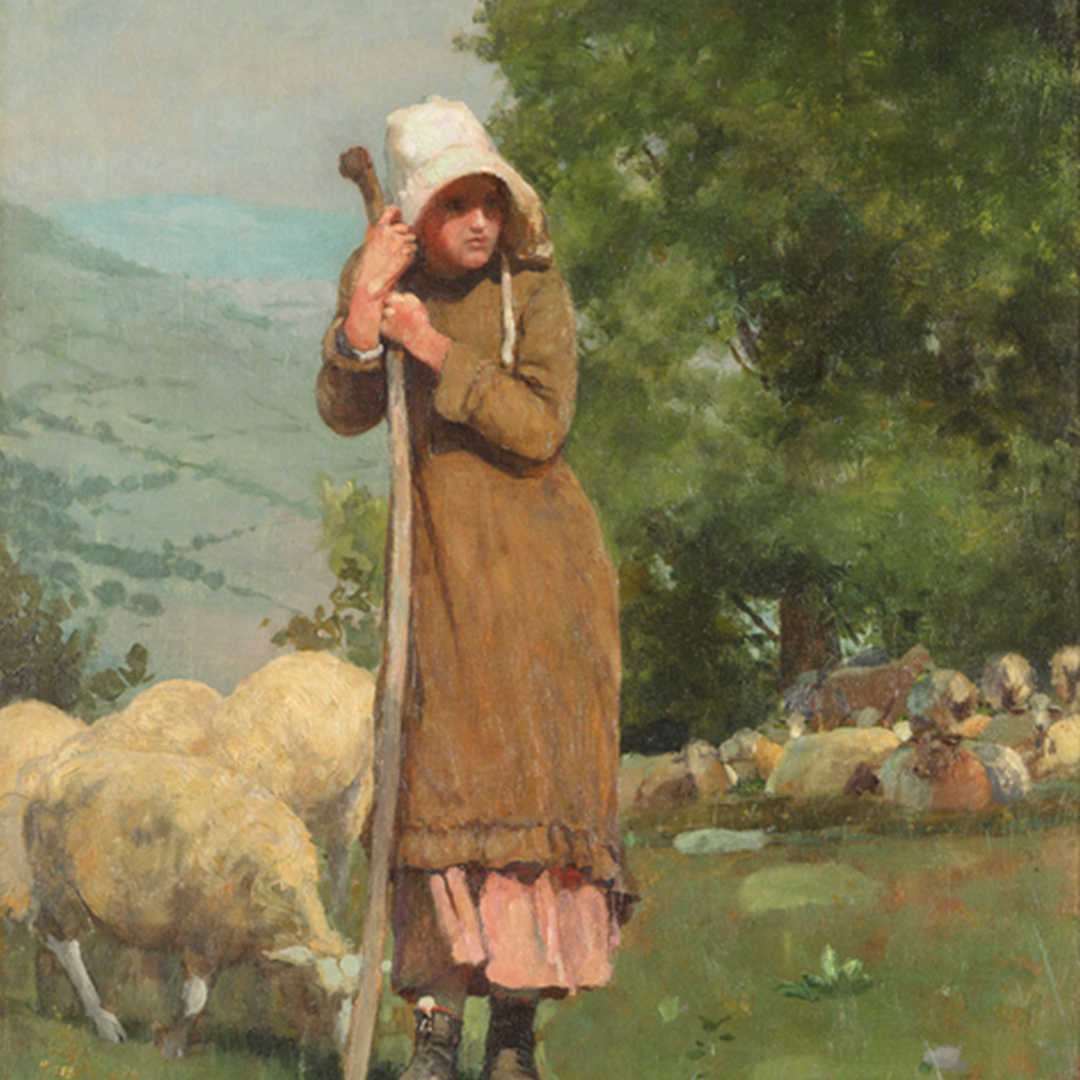
パーム砂漠のギャラリーは、エルパセオの人気のショッピング&ダイニングエリアに隣接し、カリフォルニア州のパームスプリングスエリアに位置しています。私たちの顧客は、戦後、現代美術、現代美術の私たちの選択に感謝しています。冬の間の豪華な天候は、私たちの美しい砂漠を見て、私たちのギャラリーに立ち寄るために、世界中からの訪問者を引き付けます。外の山岳砂漠の風景は、内部で待っている視覚的なごちそうに完璧な風光明媚な背景を提供します。
45188 ポルトラ・アベニュー
パーム砂漠, CA 92260
(760) 346-8926
営業時間:
月~土 9時~17時
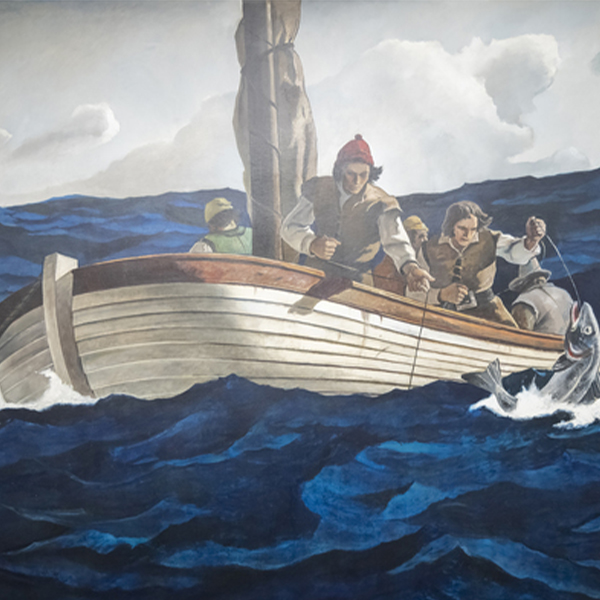
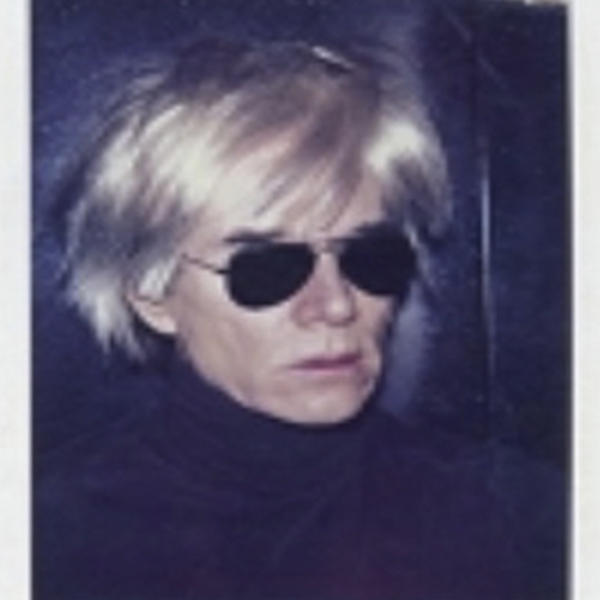
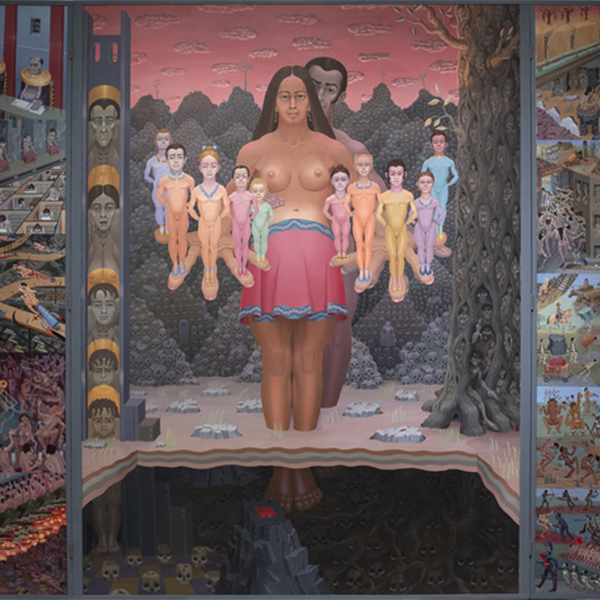
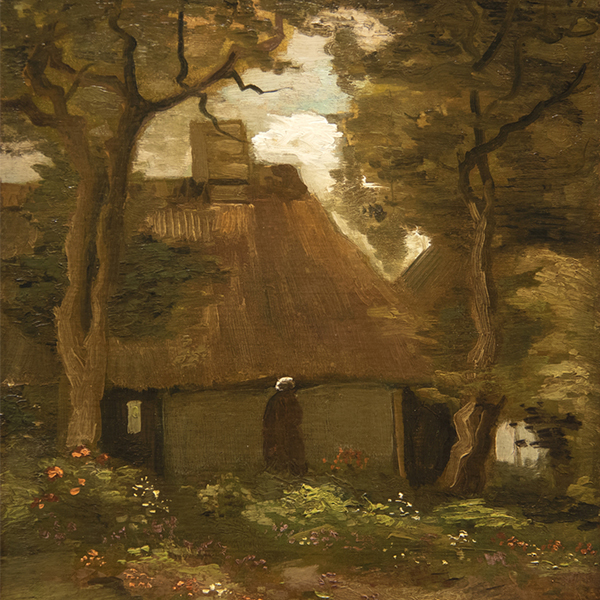
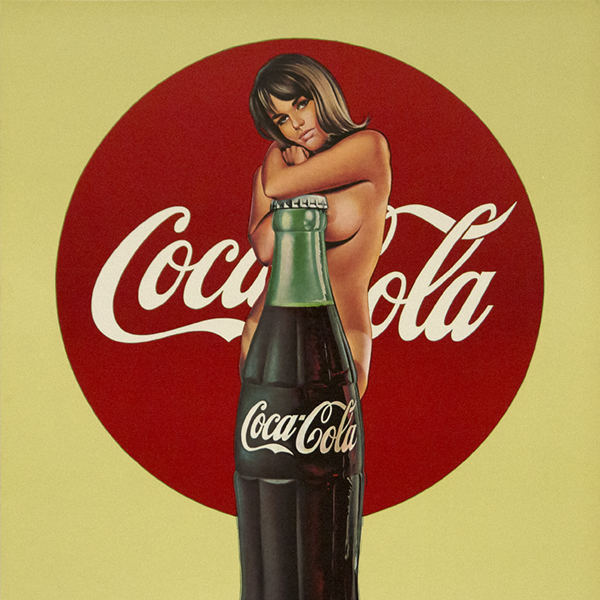
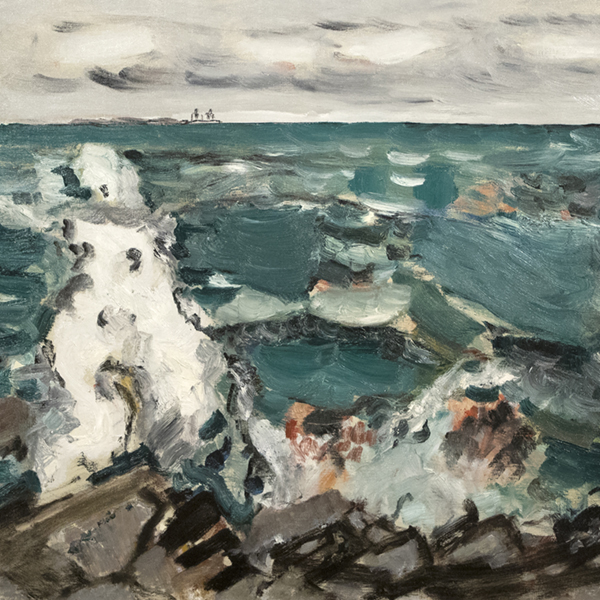
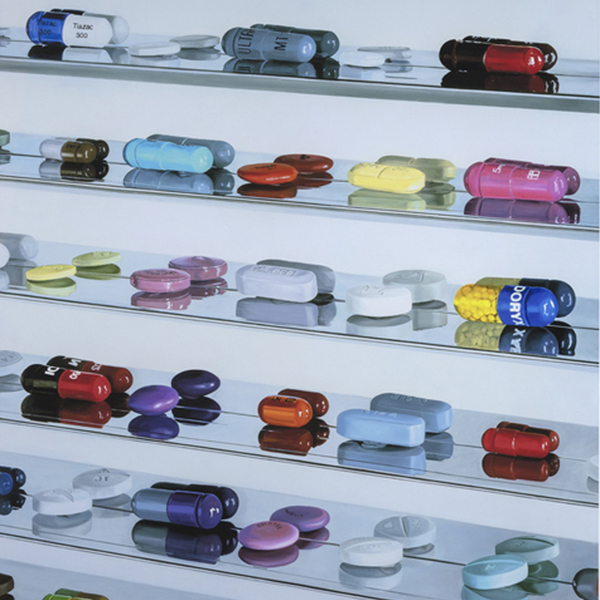


























































_tn45733.jpg )


_tn27035.jpg )


_tn27843.jpg )




_tn43322.jpg )
_tn43321.jpg )






_tn43320.jpg )



_tn28596.jpg )













_tn40803.jpg )


_tn36185.jpg )





_tn37425.jpg )




_tn45983.jpg )






























,_new_mexico_tn40147.jpg )




_tn45742.jpg )


_tn43950.jpg )
_tn45731.jpg )
_tn45739.b.jpg )


_tn45741.jpg )

_tn40169.jpg )
![SIR WINSTON CHURCHILL-Loch Choire, Scotland (C51) Painted while staying at Dunrobin Castle, the estate of the Duke of Sutherland, Churchill chose to set his easel behind a tree where he likely thought of it as a framing device, adding a layer of depth, creating a stronger sense of foreground, middle ground, and background, enhancing the three-dimensionality of the picture. Churchill painted at both Dunrobin as well as the Duke’s Sutton Place estate, later the home of John Paul Getty.<br><br>As Mary Soames describes it in her book, Winston Churchill, His Life as a Painter, “1921 had been a year of heavy personal tidings” for Churchill and his family, as he lost both his mother, Jennie Cornwallis-West, and his beloved child, Marigold, aged nearly four. In a letter to his wife Clementine, Churchill wrote, “… Many tender thoughts, my darling one of you and yr sweet kittens. Alas I keep on feeling the hurt of the Duckadilly [Marigold’s pet name].” That Churchill chose to stay with the Duke and Duchess at Dunrobin just after Marigold’s death speaks to their close friendship and his fondness for the area, including Loch Choire. It is no surprise that Churchill gifted the painting to the Duke of Sutherland](/Art_Images/Small/sir_winston_churchill_loch_choire,_scotland_(c51)_tn45743.jpg )
_tn45732.jpg )

_tn45736.jpg )
_tn45745.b.jpg )
