MARIA BLANCHARD (1881-1932)









Provenance
Collection de Carmen Egea Gutierrez, nièce de l'artisteCollection privée, par ascendance
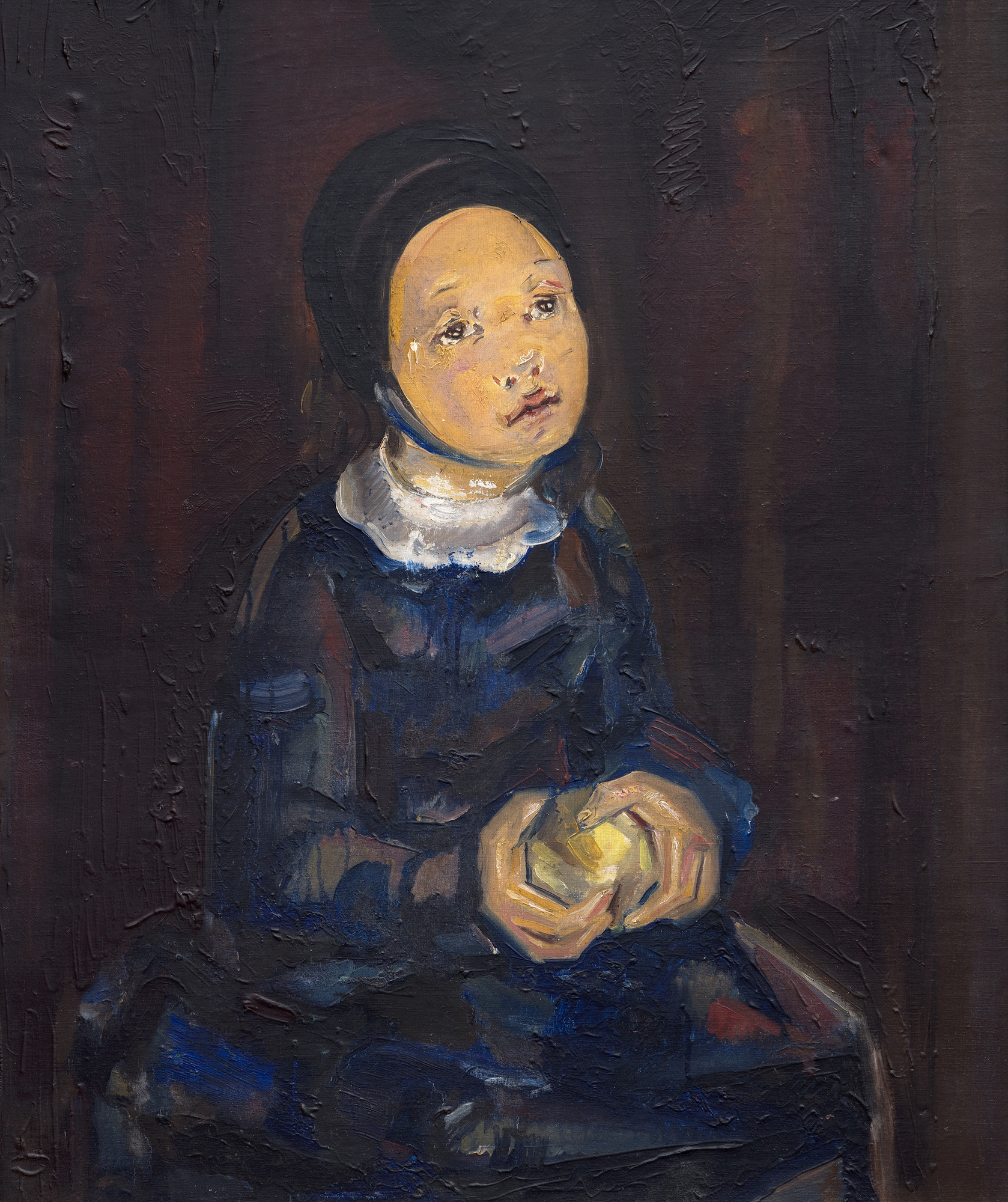
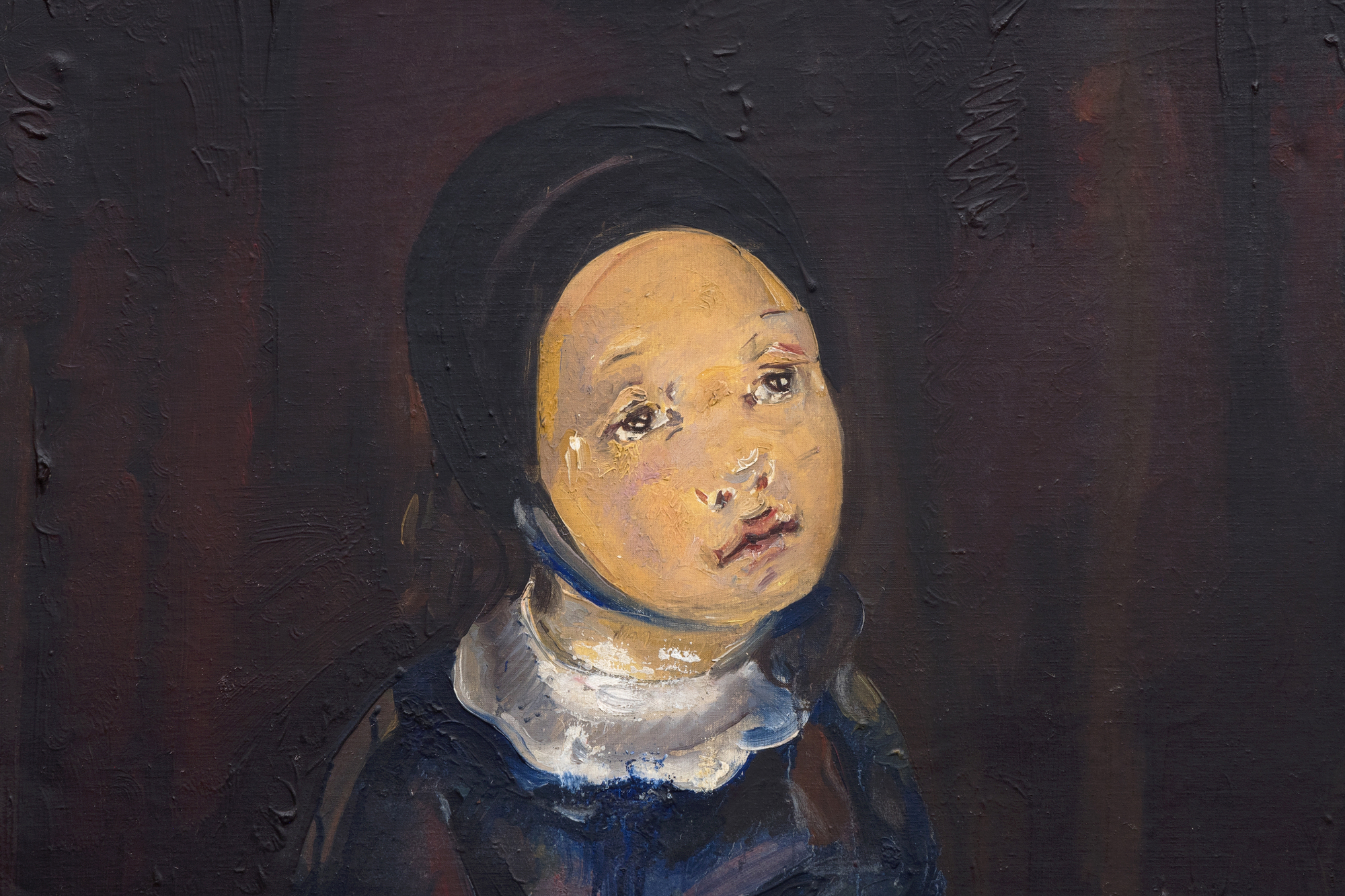
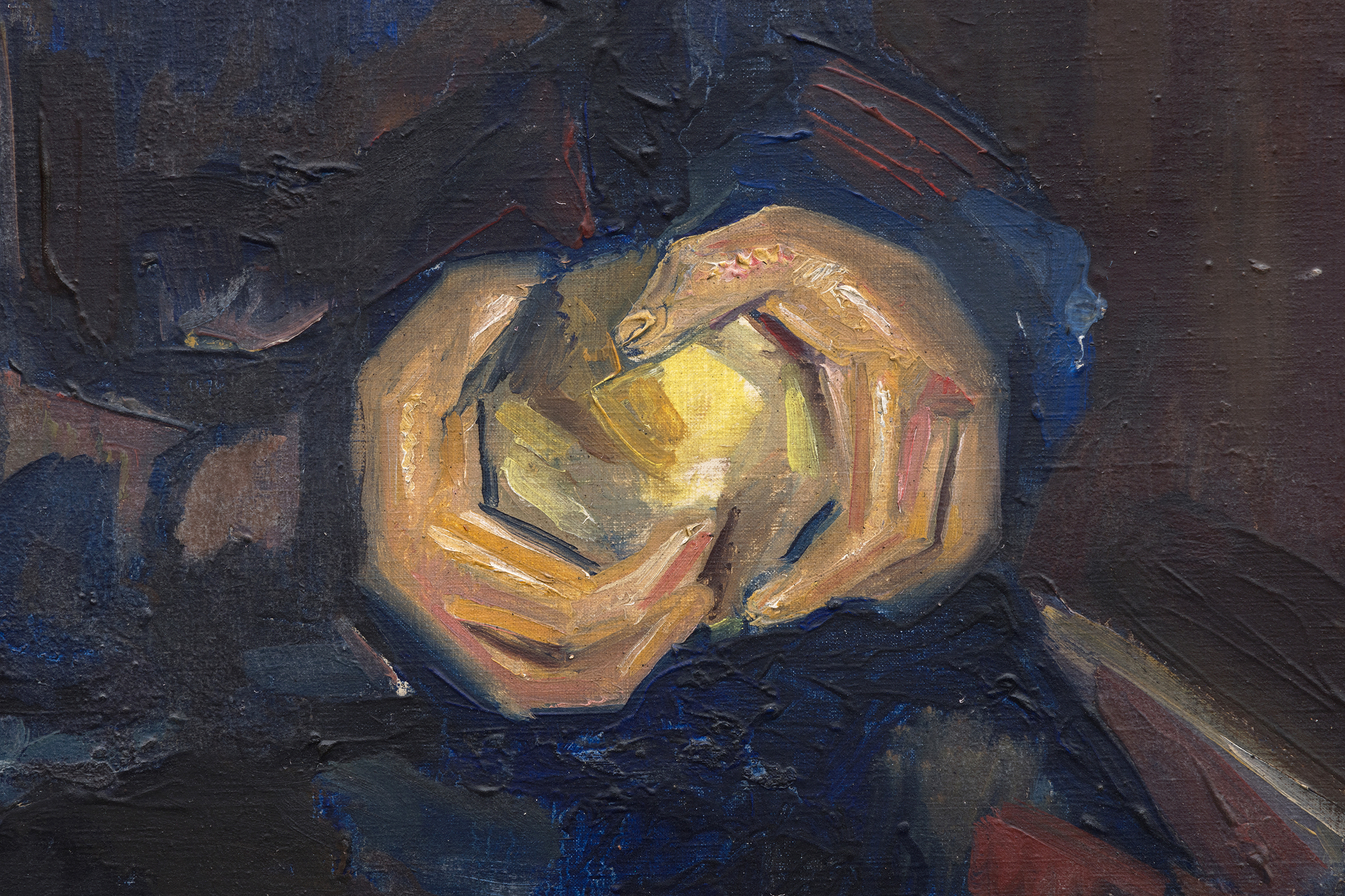
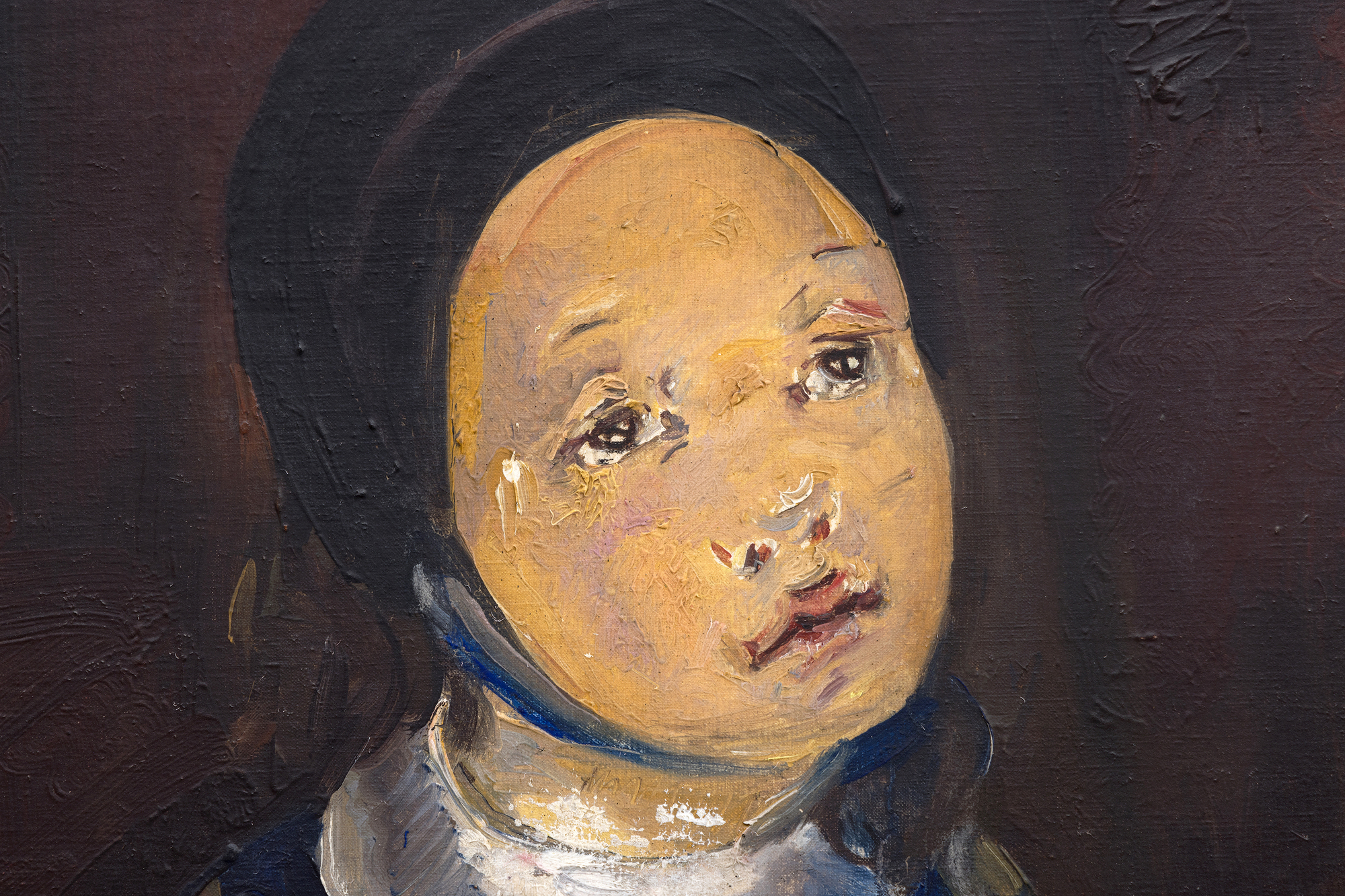
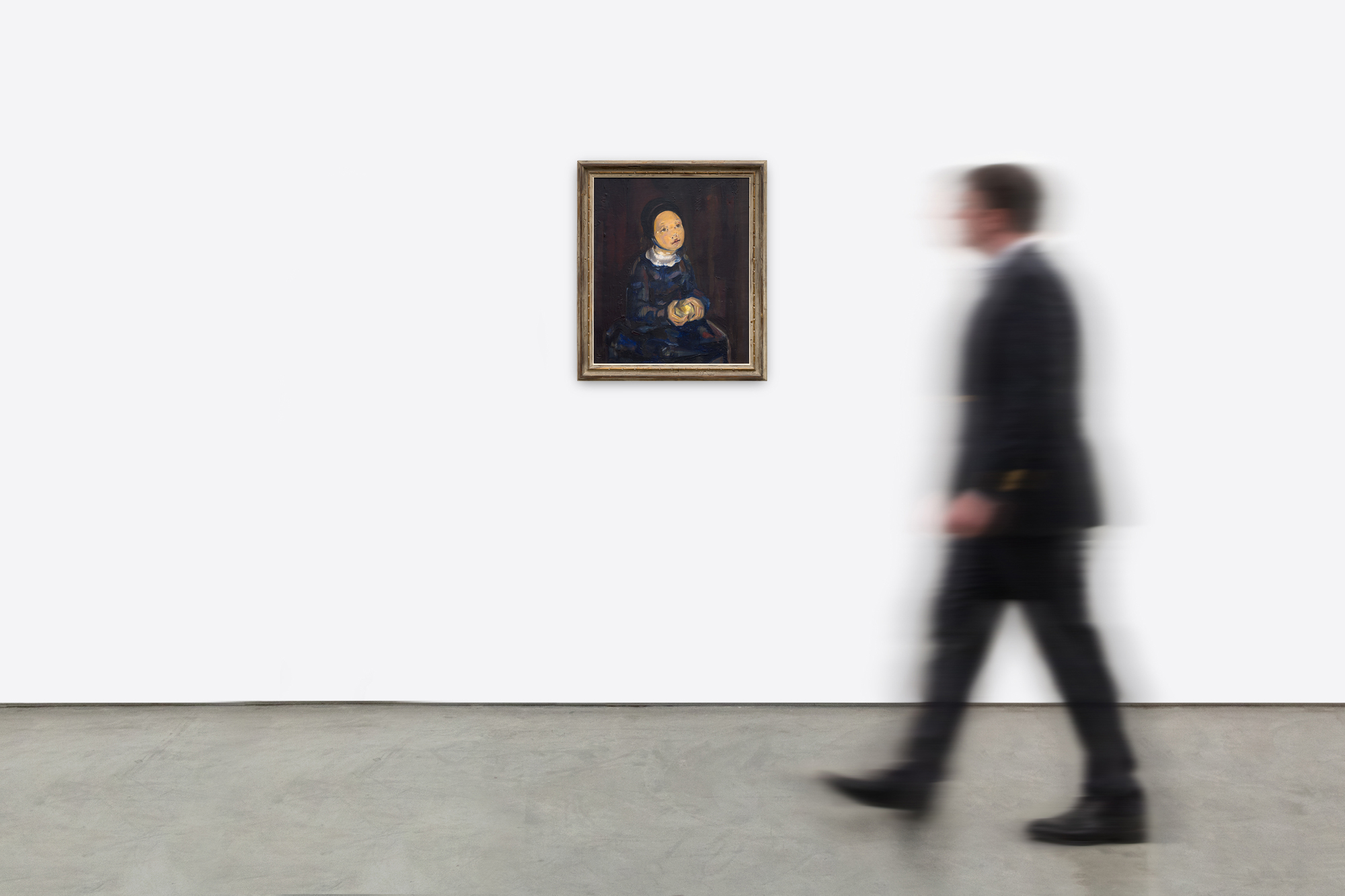
Les racines cubistes de Blanchard, proéminentes dans le traitement angulaire des mains et de la pomme, sont adoucies par la tenue modeste de la jeune fille, suggérant ainsi une signification spirituelle ou religieuse. Le visage pieux du modèle et la palette sourde de bruns, de gris et de bleus renforcent l'idée que le tableau s'inscrit dans la continuité des thèmes religieux, comme on peut le voir dans le premier chef-d'œuvre de Picasso, "La première communion", et dans l'œuvre de Blanchard, "La jeune fille à sa première communion". La pomme tenue dans la main introduit des couches de symbolisme, représentant souvent la connaissance, l'innocence ou la tentation, une association qui suggère une transition émotionnelle, faisant le pont entre l'enfance et une conscience plus profonde.
La capacité de Blanchard à fusionner la forme cubiste avec la narration symbolique et la complexité émotionnelle fait de cette peinture un reflet poignant de son évolution en tant qu'artiste. Elle humanise les formes rigides du cubisme tout en imprégnant ses sujets de profondeur et de vie intérieure.


