MARIA BLANCHARD (1881-1932)
$135,000









出所
カルメン・エゲア・グティエレス(画家の姪)のコレクションプライベート・コレクション
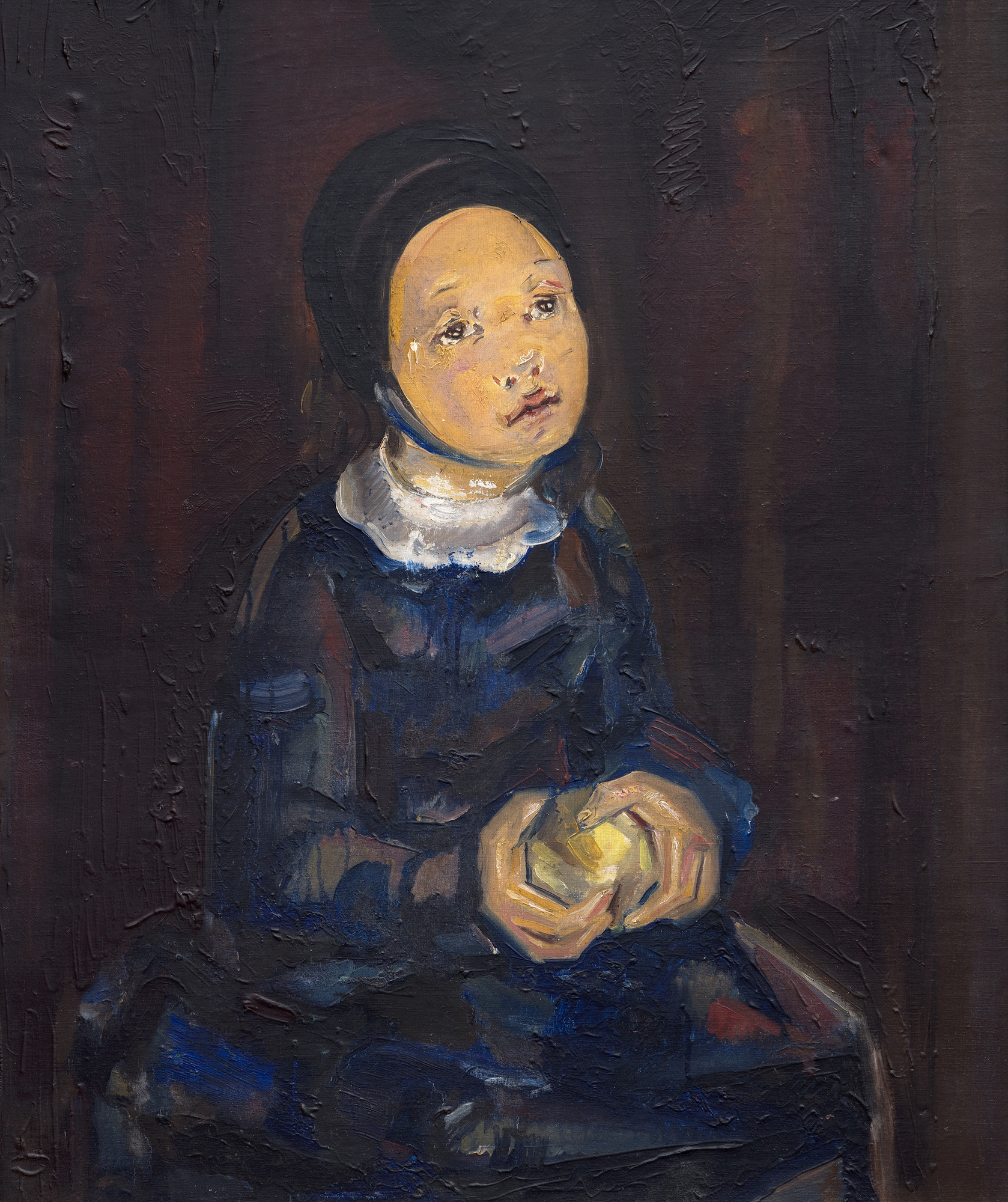
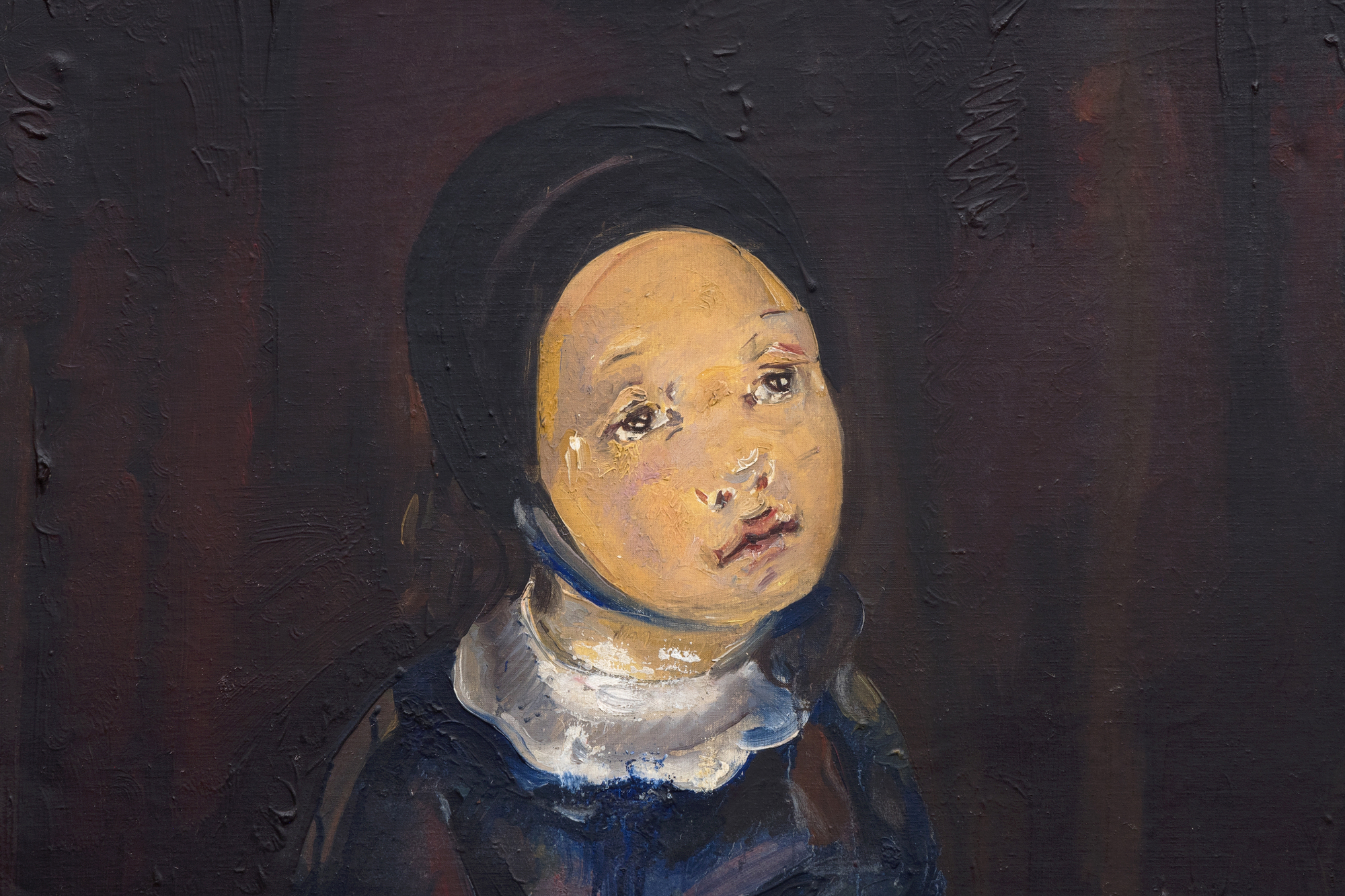
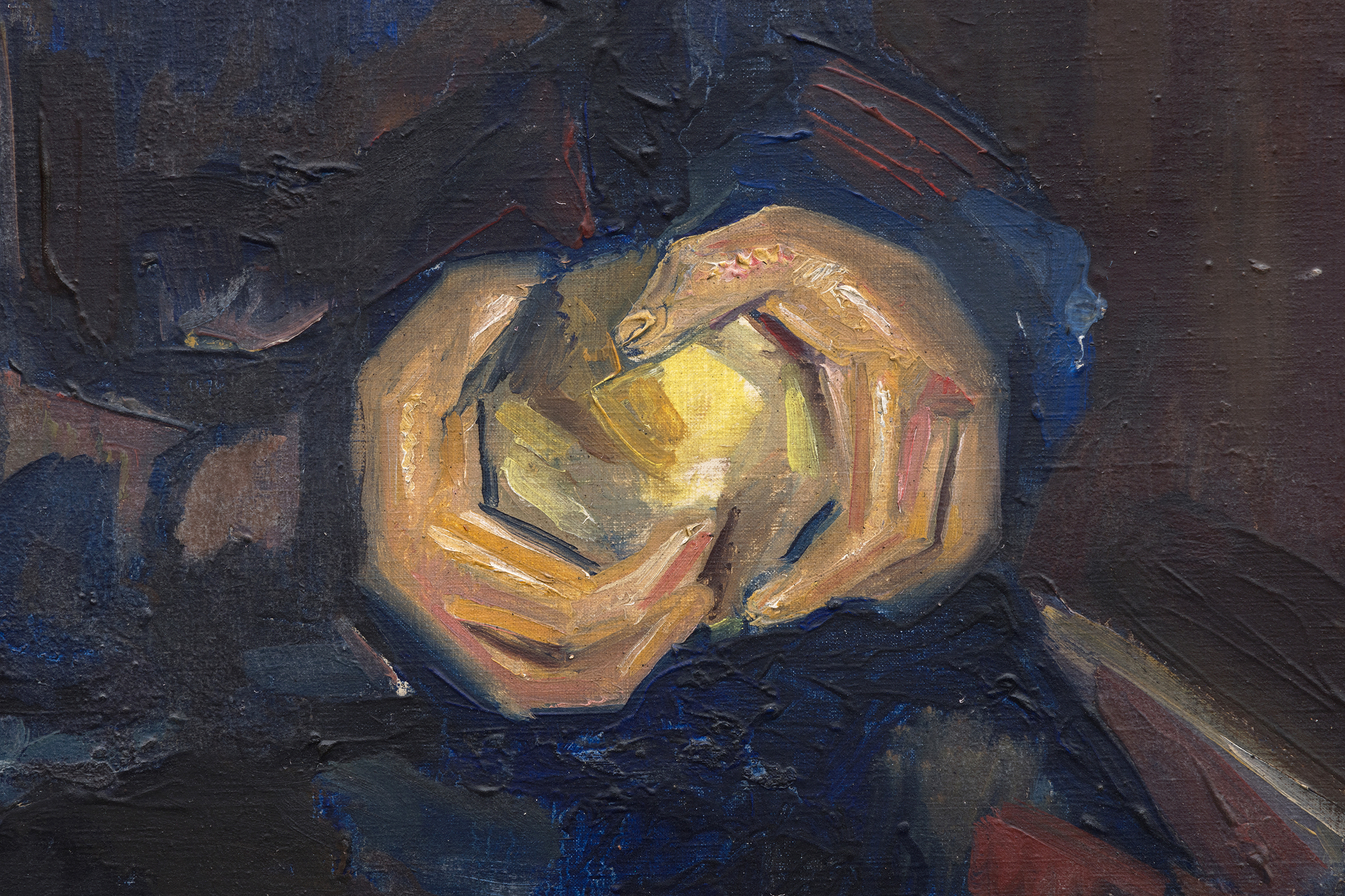
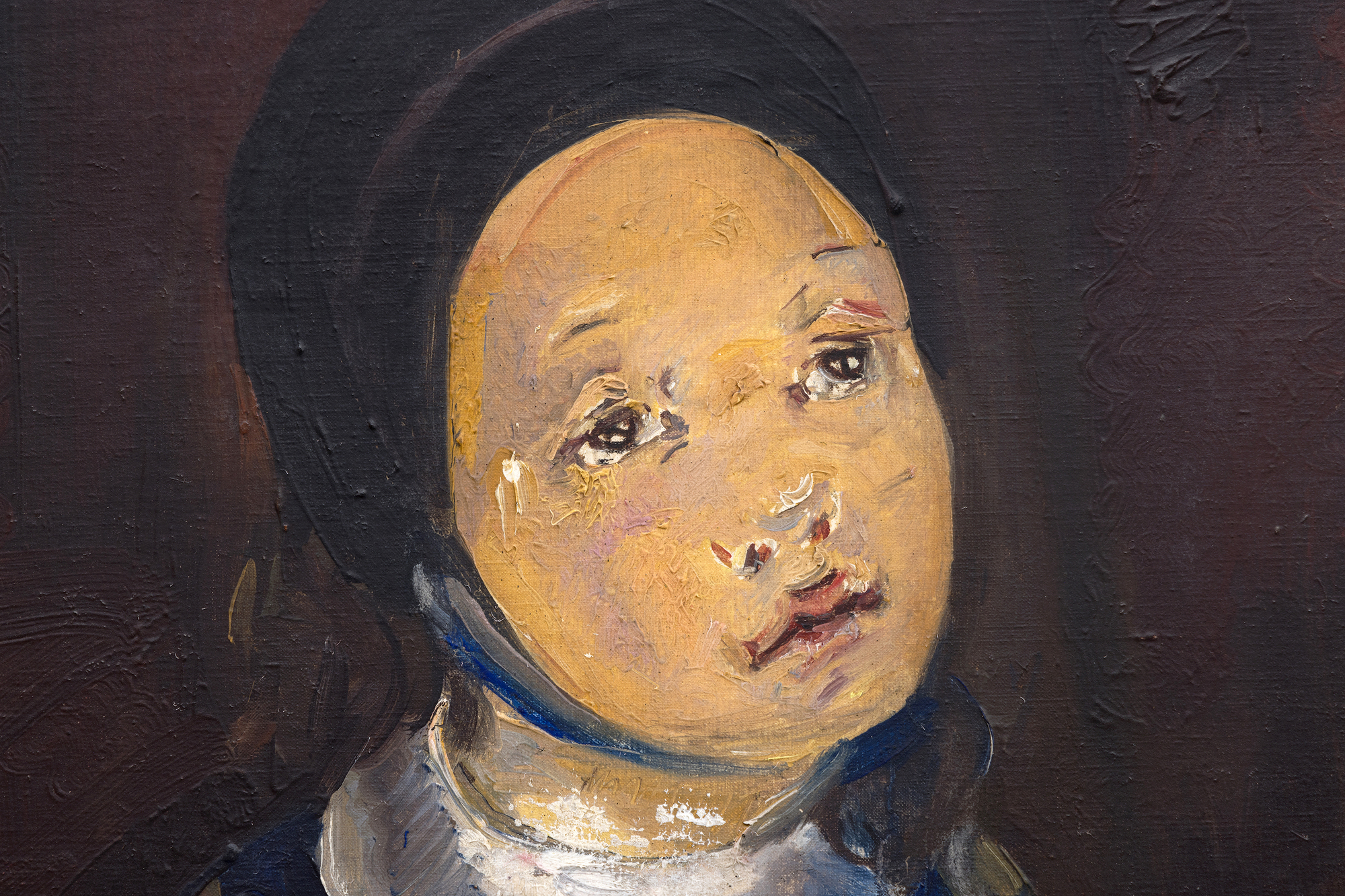
ブランシャールのキュビズムのルーツは、手とリンゴの角ばった処理に顕著に見られるが、少女の控えめな服装を通して和らげられ、精神的または宗教的な意味を示唆している。モデルの敬虔な表情と、茶色、灰色、青色の淡い色調は、ピカソの初期の代表作《初聖体》やブランシャール自身の《初聖体の少女》に見られるように、この絵が宗教的なテーマの流れを引き継いでいることをさらに強調している。手にしたリンゴは象徴の層を導入しており、しばしば知識、無邪気さ、誘惑を表し、子供時代とより深い意識との架け橋となる感情的な移行を示唆する。
ブランシャールの、キュビスムのフォルムと象徴的な物語や感情的な複雑さを融合させる能力は、この絵画を芸術家としての彼女の進化を痛切に映し出すものとなっている。彼女はキュビズムの硬質な形を人間化する一方で、被写体に深みと内面的な生命を吹き込んでいる。


