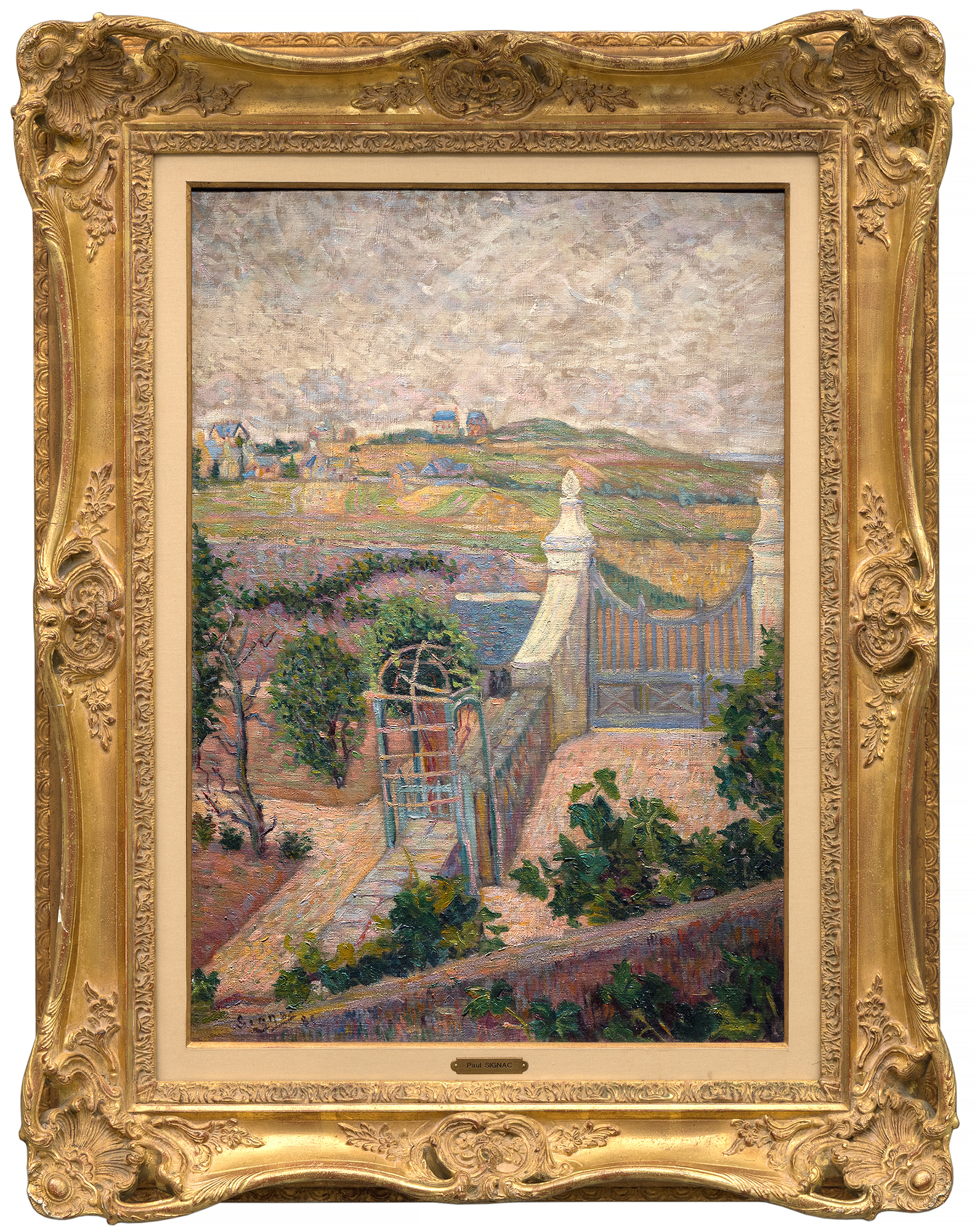
PAUL SIGNAC (1863-1935)
$425,000


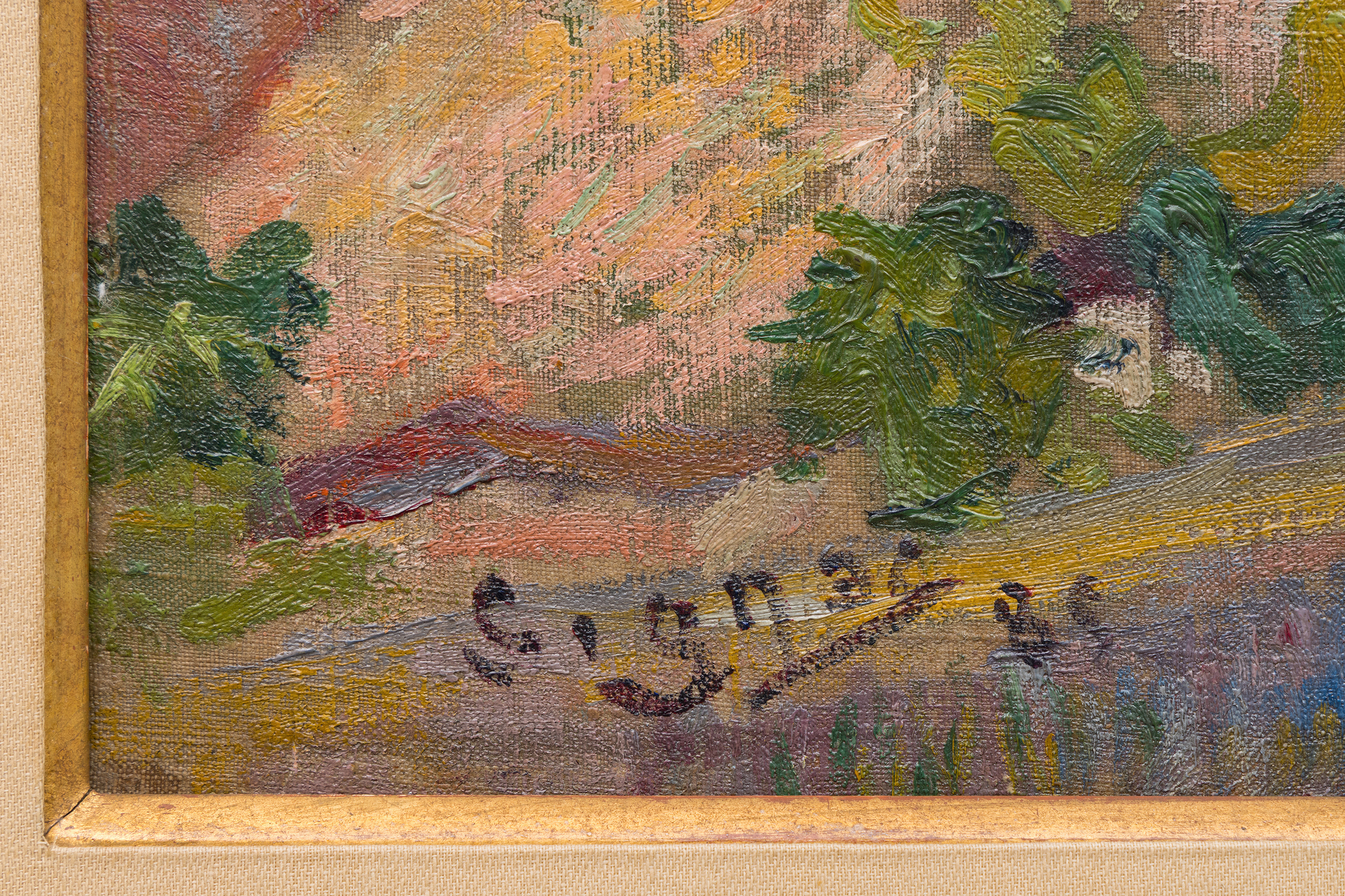

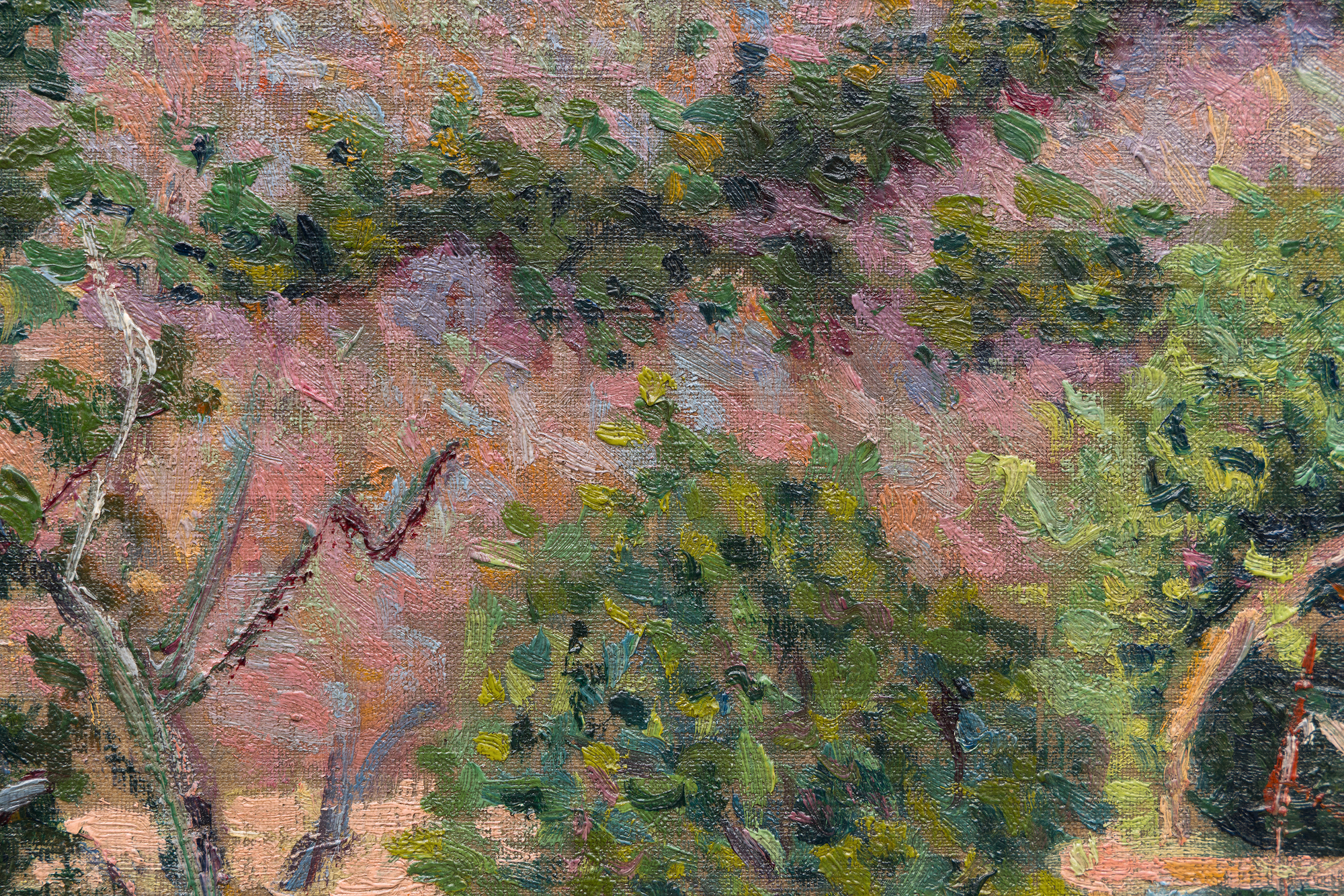



种源
儒勒-里维埃尔,卡涅巴黎德鲁奥酒店,1956年3月23日,第103号拍卖品
私人收藏,购自上文
巴黎德鲁奥酒店,1990年6月19日,拍 卖品号:130
瑞士私人收藏
2017年4月29日,慕尼黑汉普尔艺术品拍卖会,第6号拍卖品
私人收藏,购自上述作品
汉普尔艺术品拍卖行,慕尼黑,2018年9月26日,拍号602
私人收藏,购自上述作品
纽约苏富比拍卖行2023年11月14日,星期二,拍賣品號306
私人收藏,购自...更。。。以上
展会信息
纽约,美国艺术画廊,《巴黎印象派画家的油画和粉彩作品》,1886 年,第 70 号,第 18 页(标题为《从我的窗子》)。文学
Francis Soar 和 Hachette,"Connaissance des Arts",巴黎,1956 年,第 61 页。Sophie Monneret,《L'Impressionisme et son époque》,dictionnaire international,第二卷,巴黎,1980 年,第 255 页。
Drouot 酒店,《La Gazette de l'Hôtel Drouot》,第 XLIV 卷,巴黎,1990 年,第 21 期。
Françoise Cachin,Signac.油画作品目录》,巴黎,2000 年,第 102 号,第 169 页,有插图
...少。。。
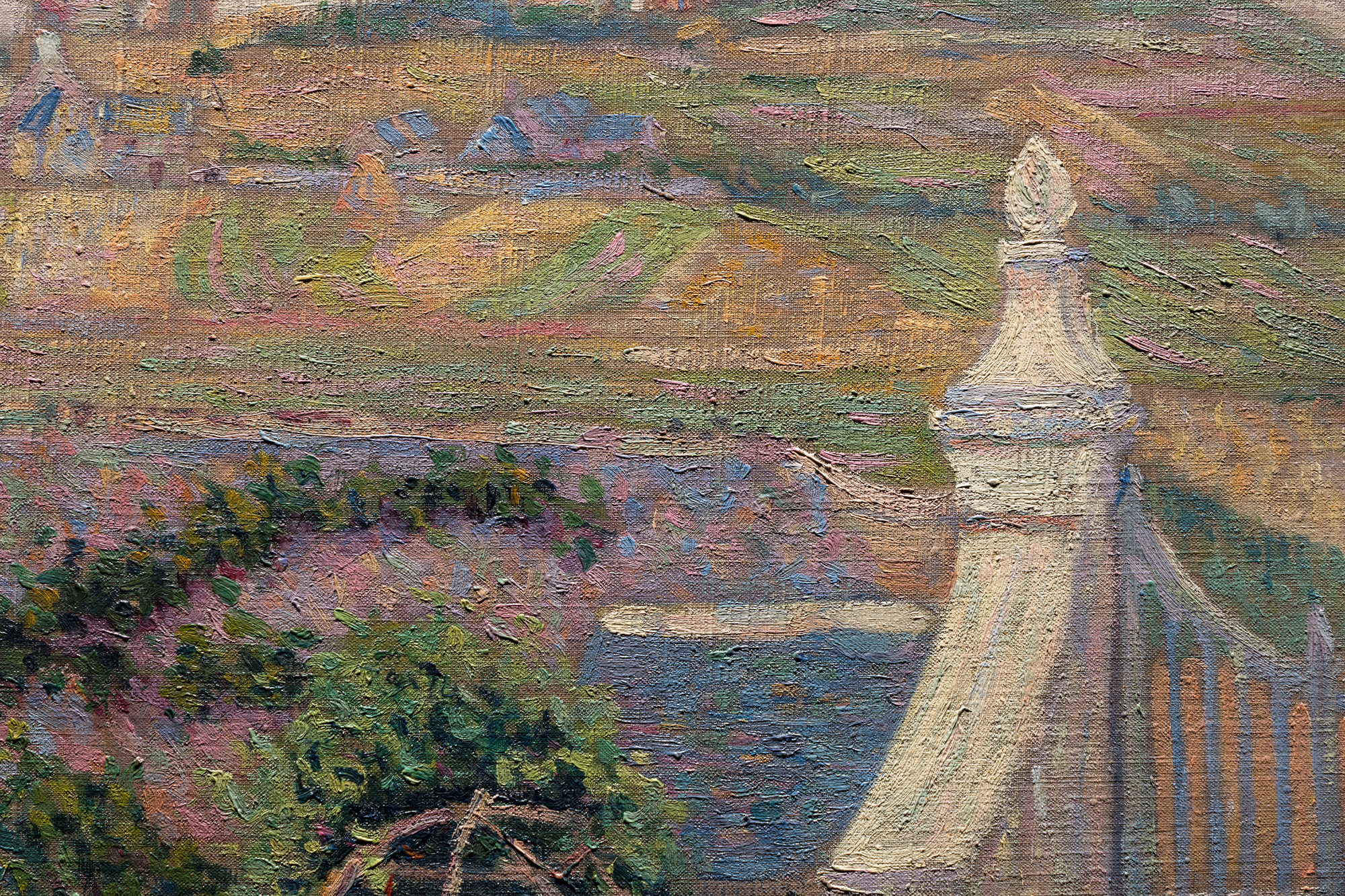
这幅作品曾属于法国作曲家兼指挥家朱尔斯-里维埃尔,并在主要艺术史著作中有所论述,包括《艺术的觉醒》(Connaissance des Arts,1956 年)、索菲-蒙内雷(Sophie Monneret)的《印象派及其时代》(L'Impressionisme et son époque,1980 年)和弗朗索瓦丝-卡尚(Françoise Cachin)的《西尼亚克》:目录》(Catalogue raisonné de l'oeuvre peint)(2000 年),其中第 102 号条目为该作品的插图。102.大都会艺术博物馆、芝加哥艺术学院和卡内基艺术博物馆都收藏有同一圣布里亚克系列的同类作品。总体而言,这些作品揭示了西涅克向结构明快过渡的过程,这种结构明快很快就成为新印象派的标志,并确保了他在现代绘画领军人物中的地位。


