希瑟·詹姆斯·杰克逊位于怀俄明州杰克逊霍尔的野生美景中,以国家公园为背景,十多年来为西部山脉带来了最高水平的艺术品和服务。
希瑟·詹姆斯(Heather James)迎合独特的社区,使杰克逊霍尔成为美国文化和户外无与伦比的目的地,致力于为当地人和游客提供无与伦比的艺术品和白手套服务。
172中心街,套房101
邮政信箱3580
杰克逊霍尔, WY 83001
(307) 200-6090
开放时间仅限预约,直至 2025 年 7 月 1 日
展览
图稿
顾问

ANDREA RICO DAHLIN
高级副总裁
怀俄明州杰克逊霍尔
Andrea 拥有纽约宾汉姆顿大学艺术史学士学位,辅修美术,并在纽约佳士得教育集团获得现代艺术、鉴赏和艺术市场史硕士学位。她曾在堪萨斯城奈尔森-阿特金斯艺术博物馆(Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art)和纽约佳士得拍卖行工作,积累了丰富的博物馆和拍卖行工作经验。
自2015年加入希瑟-詹姆斯美术公司以来,安德烈亚已经获得了寄售,并帮助重要艺术家建立了引人注目的私人和博物馆收藏,其中包括克劳德-莫奈、阿尔弗雷德-西斯利、亨利-马蒂斯、埃德加-德加、诺曼-洛克威尔、安德鲁-怀斯、伊莱恩-德库宁、安迪-沃霍尔和汤姆-韦塞尔曼。

萨拉-菲舍尔
咨询委员会联合主席
怀俄明州杰克逊霍尔
莎拉从小在艺术的熏陶下长大,对艺术和历史都有着深厚的感情。十多年来,她凭借对艺术的热爱,在画廊、拍卖行和博物馆中游刃有余。
莎拉坚信学习和体验业务的方方面面,她在艺术界担任过各种职务,为咨询和工作带来了全面的方法。自 2015 年以来,莎拉一直是 Heather James Fine Art 的关键人物,她为客户提供顶级服务,管理杰克逊霍尔画廊,策划画廊展览和收藏家之家,并带头开展战略推广活动。
莎拉在纽约大学获得了新闻学和艺术史学位,随后又在伦敦佳士得艺术、法律和商业项目中获得了硕士学位,为她的学术生涯打下了坚实的基础。除了在专业和教育方面的追求,萨拉还积极参与与她关系密切的事业,包括担任杰克逊霍尔公共艺术(Jackson Hole Public Art)董事会成员和美国大屠杀纪念博物馆(United States Holocaust Memorial Museum)董事。
作为联席主席,Sarah 将她在艺术和收藏方面的个人经验和知识融入到每一次互动中,始终为客户的需求寻求最佳解决方案。




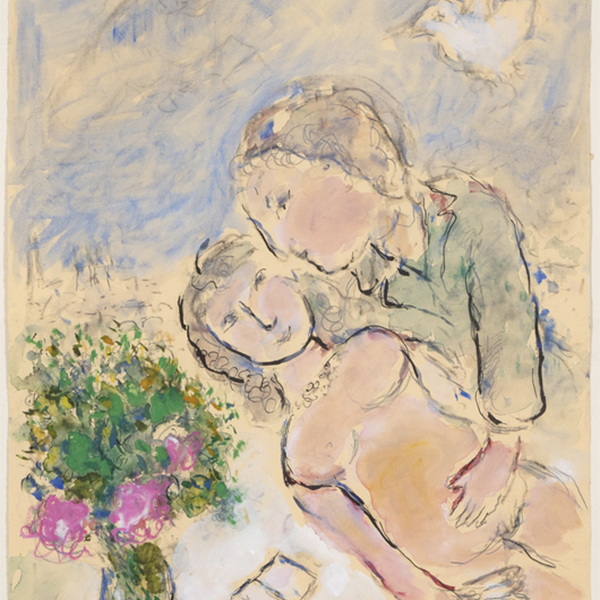







_tn43950.jpg )


















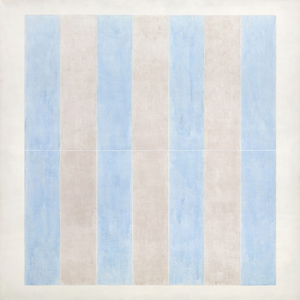
_tn46616.jpg )

_tn47464.jpg )
















































_tn47012.jpg )
,_new_mexico_tn40147.jpg )





