لي كراسنر(1908-1984)
$195,000









الاصل
معرض مارلبورومجموعة خاصة، تم اقتناؤها من المقتنيات المذكورة أعلاه، حوالي 1970
مجموعة خاصة
الادب
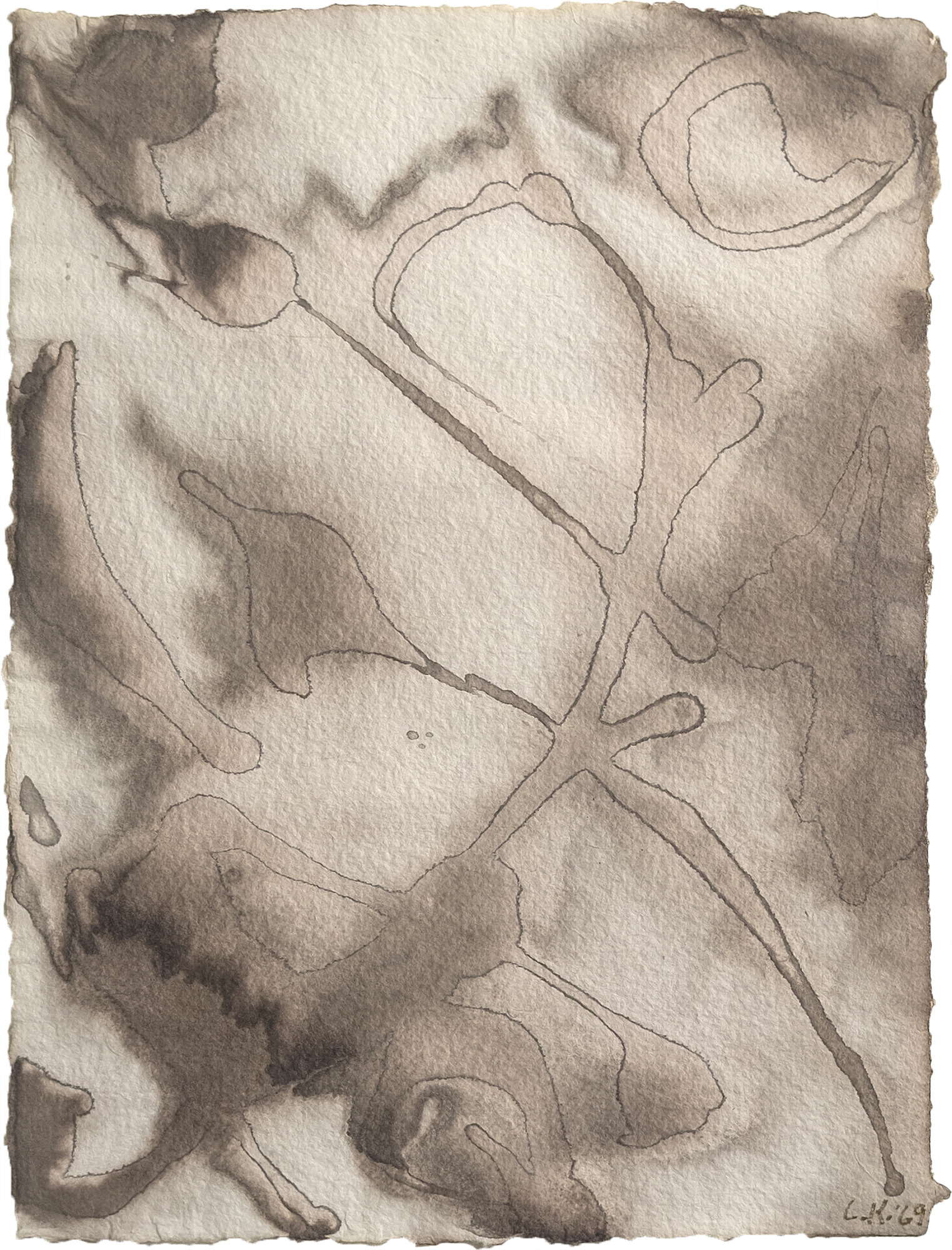
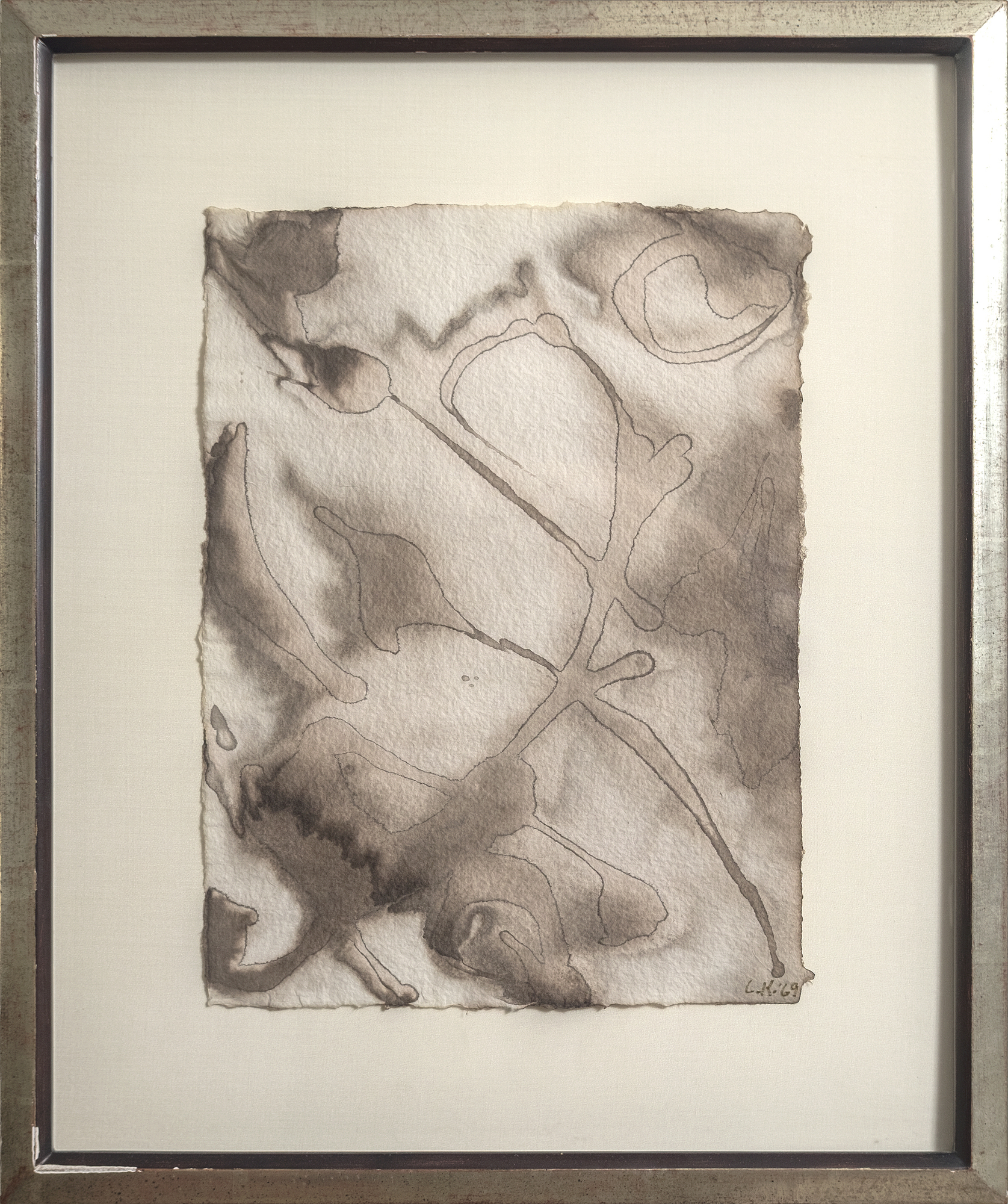
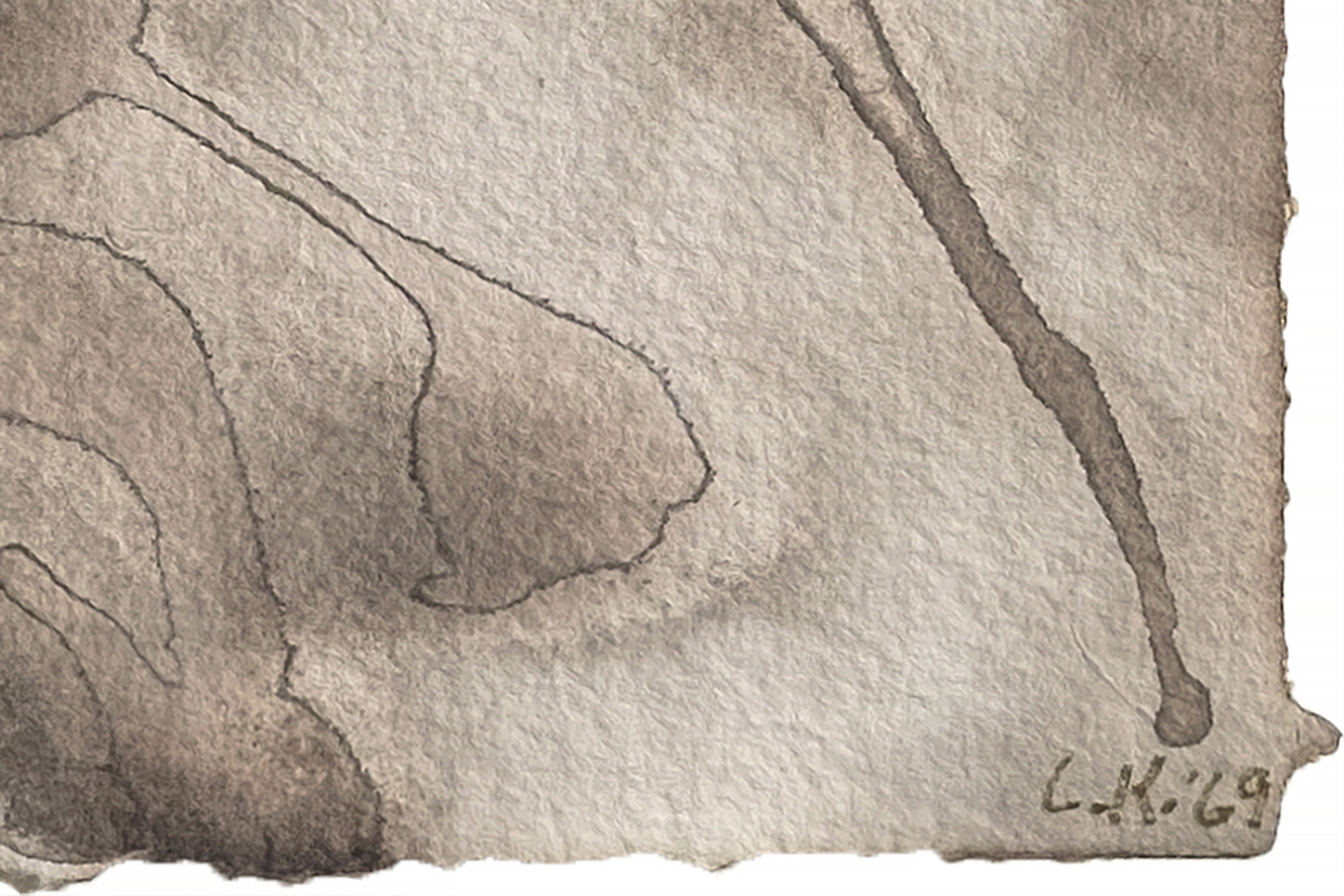
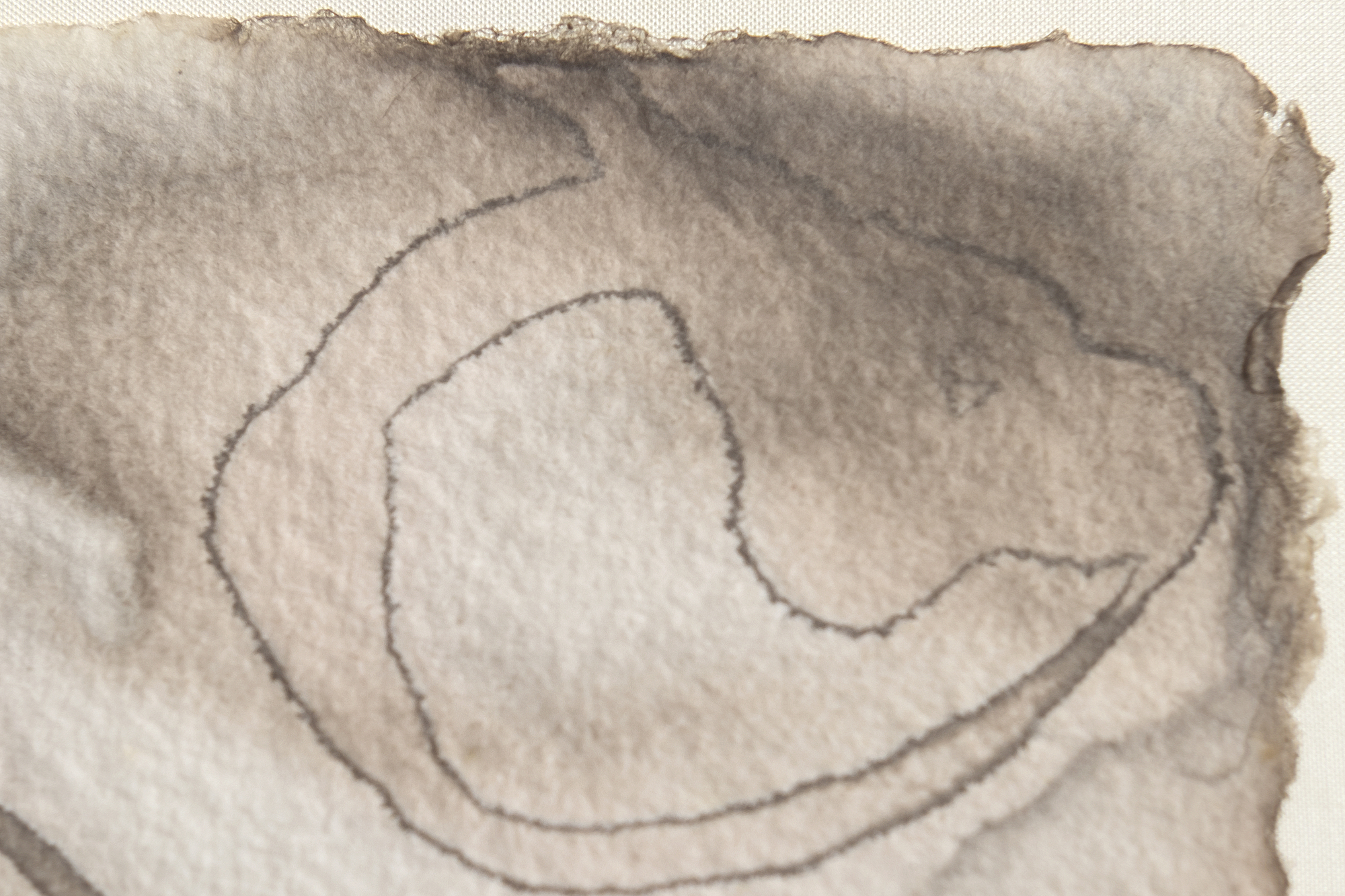
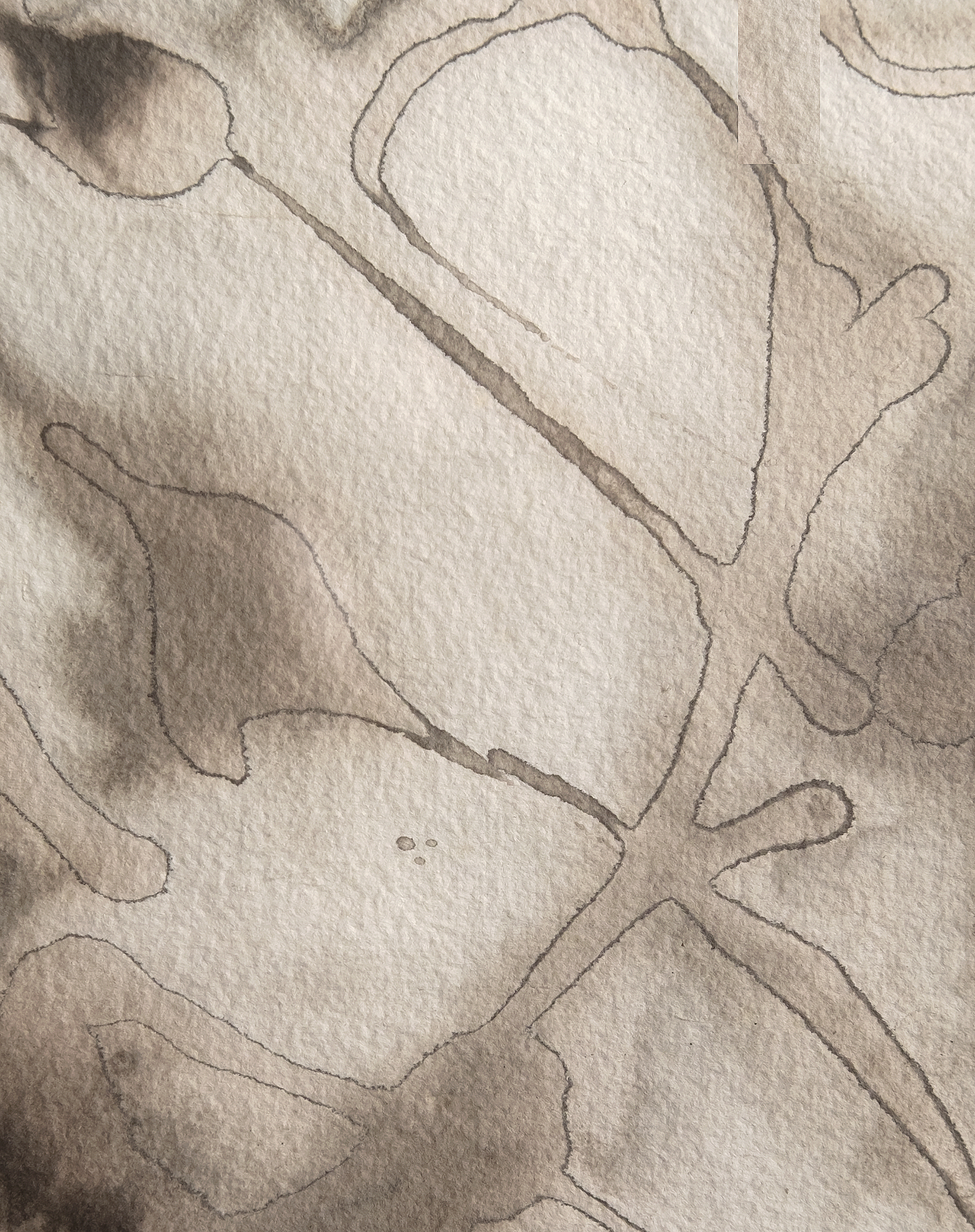
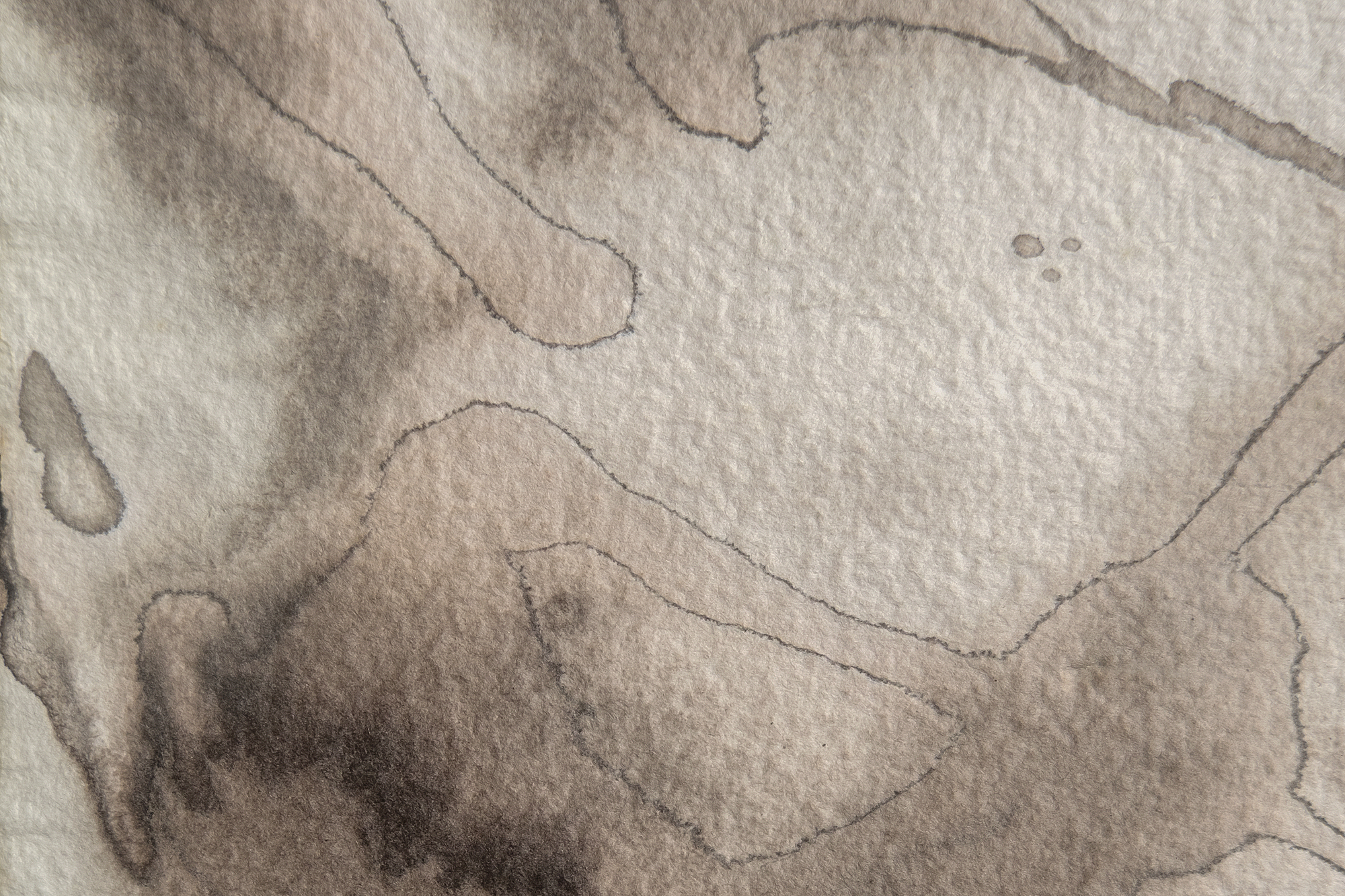
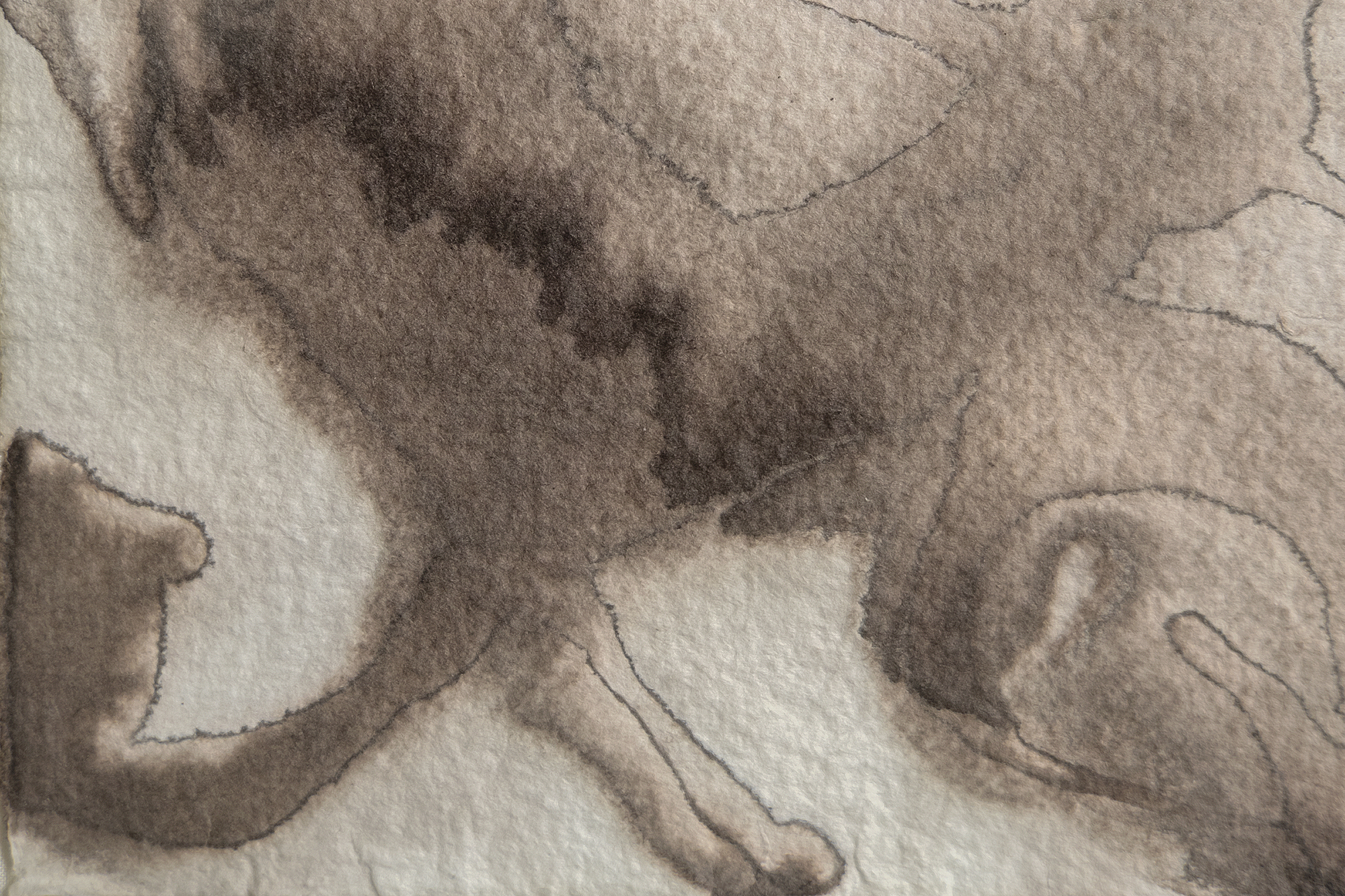
لانداو، إلين ج.، لي كراسنر: A Catalogue Raisonné، نيويورك: Abrams, 1995, p. 254, illus. 511تشير الشفافية الباهرة في أعمال مثل "الماء رقم 5" التي صُنفت على أنها "غواش على الورق" إلى أن كراسنر استخدمت تقنيات الألوان المائية التقليدية لخلق تأثيرات أكثر كثافة وعتامة ترتبط غالبًا بالغواش. يمكن للفنانين تحقيق هذا التعتيم بالألوان المائية عن طريق زيادة نسبة الصبغة إلى الماء أو وضع طبقات من الغسالات الشفافة للحصول على العمق أو استخدام أصباغ معرضة بشكل طبيعي للتحبيب والتشبع. كما عزز اختيار كراسنر لورق هاول المعروف بـ"أسنانه" المتوسطة إلى الخشنة هذه التأثيرات، حيث إن قوامه ينثر الضوء لإعطاء الأصباغ مظهرًا أكثر صلابة. تُظهر هذه التقنيات إتقان كراسنر لموادها ونهجها العملي البديهي في التجريب، مما سمح لها بتوسيع الإمكانيات التعبيرية للألوان المائية دون الاعتماد فقط على الغواش.
لم تكن كراسنر وحدها التي وجدت الإلهام في المناظر الطبيعية في لونغ آيلاند. فقد استجاب جارها، فيليم دي كونينغ، بالمثل لحيوية الشاطئ، مترجماً إيقاعاته المتموجة في أعماله في الستينيات. ومع ذلك، تفتقر سلسلة "الماء" بالنسبة لكراسنر إلى الإشارات التصويرية، وتعتمد فقط على قدرتها على التقاط الطاقة التحويلية للطبيعة من خلال التجريد. مع لوحة "الماء رقم 5"، حققت كراسنر توليفة عميقة من التقنية والرؤية، ودمجت القوة التأملية لمحيطها مع الطاقة الديناميكية لممارستها الفنية، مؤكدةً بذلك على مكانتها كقوة رائدة في الفن الأمريكي في فترة ما بعد الحرب.


